A Stk4-Foxp3-NF-κB p65 transcriptional complex promotes Treg cell activation and homeostasis
- PMID: 36149942
- PMCID: PMC9816918
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abl8357
A Stk4-Foxp3-NF-κB p65 transcriptional complex promotes Treg cell activation and homeostasis
Abstract
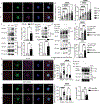
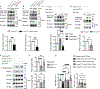
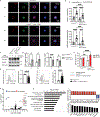
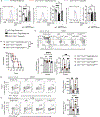
The molecular programs involved in regulatory T (Treg) cell activation and homeostasis remain incompletely understood. Here, we show that T cell receptor (TCR) signaling in Treg cells induces the nuclear translocation of serine/threonine kinase 4 (Stk4), leading to the formation of an Stk4-NF-κB p65-Foxp3 complex that regulates Foxp3- and p65-dependent transcriptional programs. This complex was stabilized by Stk4-dependent phosphorylation of Foxp3 on serine-418. Stk4 deficiency in Treg cells, either alone or in combination with its homolog Stk3, precipitated a fatal autoimmune lymphoproliferative disease in mice characterized by decreased Treg cell p65 expression and nuclear translocation, impaired NF-κB p65-Foxp3 complex formation, and defective Treg cell activation. In an adoptive immunotherapy model, overexpression of p65 or the phosphomimetic Foxp3S418E in Stk3/4-deficient Treg cells ameliorated their immune regulatory defects. Our studies identify Stk4 as an essential TCR-responsive regulator of p65-Foxp3-dependent transcription that promotes Treg cell-mediated immune tolerance.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bennett CL, Christie J, Ramsdell F, Brunkow ME, Ferguson PJ, Whitesell L, Kelly TE, Saulsbury FT, Chance PF, Ochs HD, The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat Genet 27, 20–21 (2001). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

