Predictors of the Initiation of Islet Autoimmunity and Progression to Multiple Autoantibodies and Clinical Diabetes: The TEDDY Study
- PMID: 36150053
- PMCID: PMC9643148
- DOI: 10.2337/dc21-2612
Predictors of the Initiation of Islet Autoimmunity and Progression to Multiple Autoantibodies and Clinical Diabetes: The TEDDY Study
Abstract
Objective: To distinguish among predictors of seroconversion, progression to multiple autoantibodies and from multiple autoantibodies to type 1 diabetes in young children.
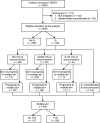
Research design and methods: Genetically high-risk newborns (n = 8,502) were followed for a median of 11.2 years (interquartile range 9.3-12.6); 835 (9.8%) developed islet autoantibodies and 283 (3.3%) were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. Predictors were examined using Cox proportional hazards models.
Results: Predictors of seroconversion and progression differed, depending on the type of first appearing autoantibody. Male sex, Finnish residence, having a sibling with type 1 diabetes, the HLA DR4 allele, probiotic use before age 28 days, and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs689_A (INS) predicted seroconversion to IAA-first (having islet autoantibody to insulin as the first appearing autoantibody). Increased weight at 12 months and SNPs rs12708716_G (CLEC16A) and rs2292239_T (ERBB3) predicted GADA-first (autoantibody to GAD as the first appearing). For those having a father with type 1 diabetes, the SNPs rs2476601_A (PTPN22) and rs3184504_T (SH2B3) predicted both. Younger age at seroconversion predicted progression from single to multiple autoantibodies as well as progression to diabetes, except for those presenting with GADA-first. Family history of type 1 diabetes and the HLA DR4 allele predicted progression to multiple autoantibodies but not diabetes. Sex did not predict progression to multiple autoantibodies, but males progressed more slowly than females from multiple autoantibodies to diabetes. SKAP2 and MIR3681HG SNPs are newly reported to be significantly associated with progression from multiple autoantibodies to type 1 diabetes.
Conclusions: Predictors of IAA-first versus GADA-first autoimmunity differ from each other and from the predictors of progression to diabetes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00279318.
© 2022 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Hummel M, Bonifacio E, Schmid S, Walter M, Knopff A, Ziegler AG. Brief communication: early appearance of islet autoantibodies predicts childhood type 1 diabetes in offspring of diabetic parents. Ann Intern Med 2004;140:882–886 - PubMed
-
- Bauer W, Veijola R, Lempainen J, et al. Age at seroconversion, HLA genotype, and specificity of autoantibodies in progression of islet autoimmunity in childhood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2019;104:4521–4530 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002535/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200700014C/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK128847/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK095300/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK117483/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK112243/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK124166/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK106955/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK100238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials