Ablation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress kinase PERK induces paraptosis and type I interferon to promote anti-tumor T cell responses
- PMID: 36150390
- PMCID: PMC9561067
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.08.016
Ablation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress kinase PERK induces paraptosis and type I interferon to promote anti-tumor T cell responses
Abstract
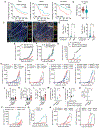
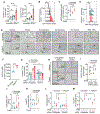
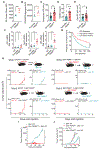
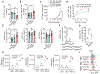
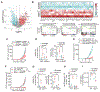
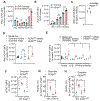
Activation of unfolded protein responses (UPRs) in cancer cells undergoing endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress promotes survival. However, how UPR in tumor cells impacts anti-tumor immune responses remains poorly described. Here, we investigate the role of the UPR mediator pancreatic ER kinase (PKR)-like ER kinase (PERK) in cancer cells in the modulation of anti-tumor immunity. Deletion of PERK in cancer cells or pharmacological inhibition of PERK in melanoma-bearing mice incites robust activation of anti-tumor T cell immunity and attenuates tumor growth. PERK elimination in ER-stressed malignant cells triggers SEC61β-induced paraptosis, thereby promoting immunogenic cell death (ICD) and systemic anti-tumor responses. ICD induction in PERK-ablated tumors stimulates type I interferon production in dendritic cells (DCs), which primes CCR2-dependent tumor trafficking of common-monocytic precursors and their intra-tumor commitment into monocytic-lineage inflammatory Ly6C+CD103+ DCs. These findings identify how tumor cell-derived PERK promotes immune evasion and highlight the potential of PERK-targeting therapies in cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: PERK; immunogenic cell death; tumor immunity; type I IFN; unfolded protein responses.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Atkins C, Liu Q, Minthorn E, Zhang SY, Figueroa DJ, Moss K, Stanley TB, Sanders B , Goetz A, Gaul N, et al. (2013). Characterization of a novel PERK kinase inhibitor with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Cancer Res. 73, 1993–2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

