Spatiotemporal pattern recognition and dynamical analysis of COVID-19 in Shanghai, China
- PMID: 36150538
- PMCID: PMC9487177
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2022.111279
Spatiotemporal pattern recognition and dynamical analysis of COVID-19 in Shanghai, China
Abstract
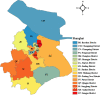
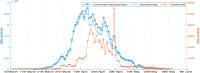
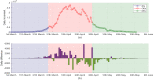
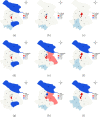
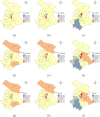
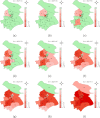
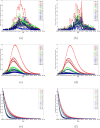
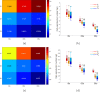
Shanghai suffered a large outbreak of Omicron mutant of COVID-19 at the beginning of March 2022. To figure out the spatiotemporal patterns of the epidemic, a retrospective statistical investigation, coupled with a dynamic model, is implemented in this study. The hotspots of SARS-CoV-2 transmissions are identified, and strong aggregative effects in the decay stage are found. Besides, the visualization of disease diffusion is provided to show how COVID-19 disease invades all districts of Shanghai in the early stage. Furthermore, the calculations from the dynamic model manifest the effect of detections to suppress the epidemic dissemination. These results reveal the strategies to improve the spatial control of disease.
Keywords: Autocorrelation analysis; Daily reproduction number; Dynamic model; Spatial statistics.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Anon . 2022. Real time big data report of epidemic situation for novel coronavirus pneumonia. https://voice.baidu.com/act/newpneumonia/newpneumonia/?from=osari_aladin.... (Accessed 31 May 2022)
-
- Anselin L. Local indicators of spatial association - LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995;27(2):93–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-4632.1995.tb00338.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

