A 3D image-based modelling approach for understanding spatiotemporal processes in phosphorus fertiliser dissolution, soil buffering and uptake by plant roots
- PMID: 36151240
- PMCID: PMC9508158
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-19047-1
A 3D image-based modelling approach for understanding spatiotemporal processes in phosphorus fertiliser dissolution, soil buffering and uptake by plant roots
Abstract
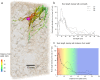
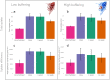
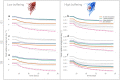
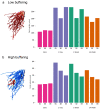
Phosphorus (P) is a key yield-limiting nutrient for crops, but the main source of P fertiliser is finite. Therefore, efficient fertilisation is crucial. Optimal P application requires understanding of the dynamic processes affecting P availability to plants, including fertiliser dissolution rate and soil buffer power. However, standard soil testing methods sample at fixed time points, preventing a mechanistic understanding of P uptake variability. We used image-based modelling to investigate the effects of fertiliser dissolution rate and soil buffer power on P uptake by wheat roots imaged using X-ray CT. We modelled uptake based on 1-day, 1-week, and 14-week dissolution of a fixed quantity of total P for two common soil buffer powers. We found rapid fertiliser dissolution increased short-term root uptake, but total uptake from 1-week matched 1-day dissolution. We quantified the large effects root system architecture had on P uptake, finding that there were trade-offs between total P uptake and uptake per unit root length, representing a carbon investment/phosphorus uptake balance. These results provide a starting point for predictive modelling of uptake from different P fertilisers in different soils. With the addition of further X-ray CT image datasets and a wider range of conditions, our simulation approach could be developed further for rapid trialling of fertiliser-soil combinations to inform field-scale trials or management.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Barber SA. Soil Nutrient Bioavailability: A Mechanistic Approach. Wiley; 1995.
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2019).
-
- Blackwell M, Darch T, Haslam R. Phosphorus use efficiency and fertilizers: Future opportunities for improvements. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2019;6:332–340. doi: 10.15302/J-FASE-2019274. - DOI
-
- Withers, P. J., Sylvester-Bradley, R., Jones, D. L., Healey, J. R. & Talboys, P. J. Feed the Crop Not the Soil: Rethinking Phosphorus Management in the Food Chain (ACS Publications, 2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

