Nanocavity-induced trion emission from atomically thin WSe2
- PMID: 36151265
- PMCID: PMC9508186
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-20226-3
Nanocavity-induced trion emission from atomically thin WSe2
Abstract
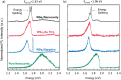
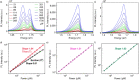
Exciton is a bosonic quasiparticle consisting of a pair of electron and hole, with promising potentials for optoelectronic device applications, such as exciton transistors, photodetectors and light emitting devices. However, the charge-neutral nature of excitons renders them challenging to manipulate using electronics. Here we present the generation of trions, a form of charged excitons, together with enhanced exciton resonance in monolayer WSe2. The excitation of the trion quasiparticles is achieved by the hot carrier transport from the integrated gold plasmonic nanocavity, formed by embedding monolayer WSe2 between gold nanoparticles and a gold film. The nanocavity-induced negatively charged trions provide a promising route for the manipulation of excitons, essential for the construction of all-exciton information processing circuits.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Manzeli S, Ovchinnikov D, Pasquier D, Yazyev OV, Kis A. 2D transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017;2:17033. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2017.33. - DOI
-
- Lv R, et al. Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides: Clusters, ribbons, sheets and more. Nano Today. 2015;10:559–592. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2015.07.004. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

