Humoral immunoresponse elicited against an adenoviral-based SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus vaccine in elderly patients
- PMID: 36152043
- PMCID: PMC9550251
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204299
Humoral immunoresponse elicited against an adenoviral-based SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus vaccine in elderly patients
Abstract
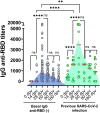
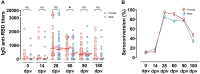
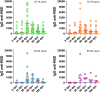
The early sequencing of the SARS-CoV-2 viral genome allowed for a speedy development of effective vaccines against the virus. Nevertheless, age-related immunosenescence, the inability to mount strong immune responses, still represents a major obstacle. Here, in a group of 149 elderly volunteers (70-96 years old), evolution of the humoral immune response over time to Gam-COVID-Vac (Sputnik V), a vaccine based on heterologous recombinant adenovirus-26 (Ad26) and adenovirus-5 (Ad5) carrying the Spike genome, was analyzed by an anti-RBD ELISA. At 28 days post vaccination (dpv), a seroconversion rate of 91% was achieved, showing the importance of administering at least two doses of Gam-COVID-Vac to elicit a robust immune response, especially in elderly individuals without previous SARS-CoV-2 infection. Interestingly, IgG specific antibodies that reached their highest titers around 28 dpv (median = 740), persisted without significant decrease after 60 dpv (median = 650). After 90 dpv, IgG titers began to drop, and at 180 dpv only 44.7% of the elderly individuals remained with detectable anti-RBD IgG antibodies. No significant differences were observed in specific humoral immune responses between genders at early times point. However, at 60 dpv anti-RBD titers were more persistent in elderly females, and only dropped at 90 dpv (p < 0.0001). As expected, the highest antibodies titers were elicited in the youngest subgroup (70-74 years). Our results show that Gam-COVID-Vac was able to deal with the ageing of the immune system, eliciting a robust immune response in an elderly cohort, which lasted approximately 90 dpv at high levels, and protected against COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Gam-COVID-Vac; SARS-CoV-2; elderly; humoral immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assessment of the humoral response to the homologous Gam-COVID-Vac (Sputnik V) or heterologous Sputnik V/mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in dialysis patients.J Nephrol. 2023 Apr;36(3):861-872. doi: 10.1007/s40620-022-01446-2. Epub 2022 Sep 24. J Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36152219 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term analysis of antibodies elicited by SPUTNIK V: A prospective cohort study in Tucumán, Argentina.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022 Feb;6:100123. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2021.100123. Epub 2021 Nov 20. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022. PMID: 34841388 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Profiling of In Vitro Reactivated Memory B Cells Following Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Gam-COVID-Vac Vaccination.Cells. 2022 Jun 21;11(13):1991. doi: 10.3390/cells11131991. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805076 Free PMC article.
-
Tapping the immunological imprints to design chimeric SARS-CoV-2 vaccine for elderly population.Int Rev Immunol. 2022;41(4):448-463. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2021.1925267. Epub 2021 May 12. Int Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 33978550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the humoral immune response during COVID-19: guilty or not guilty?Mucosal Immunol. 2022 Jun;15(6):1170-1180. doi: 10.1038/s41385-022-00569-w. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Mucosal Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36195658 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
mRNA and Adenoviral Vector Vaccine Platforms Utilized in COVID-19 Vaccines: Technologies, Ecosystem, and Future Directions.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Nov 21;11(12):1737. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11121737. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38140142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developing the next-generation of adenoviral vector vaccines.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025 Dec;21(1):2514356. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2514356. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40590260 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

