c-Myc plays a key role in IFN-γ-induced persistence of Chlamydia trachomatis
- PMID: 36155135
- PMCID: PMC9512400
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.76721
c-Myc plays a key role in IFN-γ-induced persistence of Chlamydia trachomatis
Abstract
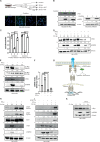
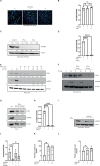
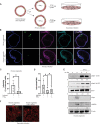
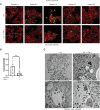
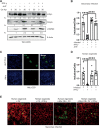
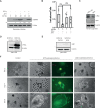
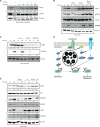
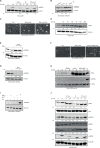
Chlamydia trachomatis (Ctr) can persist over extended times within their host cell and thereby establish chronic infections. One of the major inducers of chlamydial persistence is interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) released by immune cells as a mechanism of immune defence. IFN-γ activates the catabolic depletion of L-tryptophan (Trp) via indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), resulting in persistent Ctr. Here, we show that IFN-γ induces the downregulation of c-Myc, the key regulator of host cell metabolism, in a STAT1-dependent manner. Expression of c-Myc rescued Ctr from IFN-γ-induced persistence in cell lines and human fallopian tube organoids. Trp concentrations control c-Myc levels most likely via the PI3K-GSK3β axis. Unbiased metabolic analysis revealed that Ctr infection reprograms the host cell tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle to support pyrimidine biosynthesis. Addition of TCA cycle intermediates or pyrimidine/purine nucleosides to infected cells rescued Ctr from IFN-γ-induced persistence. Thus, our results challenge the longstanding hypothesis of Trp depletion through IDO as the major mechanism of IFN-γ-induced metabolic immune defence and significantly extends the understanding of the role of IFN-γ as a broad modulator of host cell metabolism.
Keywords: Chlamydia trachomatis; c-Myc; infectious disease; interferon-gamma; microbiology; persistence.
© 2022, Vollmuth et al.
Conflict of interest statement
NV, LS, YG, PH, SJ, NK, WS, AS, KS, KR, TR No competing interests declared
Figures
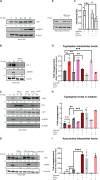
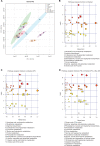
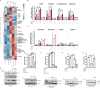
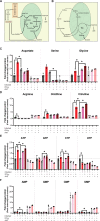
References
-
- Aiyar A, Quayle AJ, Buckner LR, Sherchand SP, Chang TL, Zea AH, Martin DH, Belland RJ. Influence of the tryptophan-indole-ifnγ axis on human genital Chlamydia trachomatis infection: role of vaginal co-infections. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 2014;4:72. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00072. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albert T, Urlbauer B, Kohlhuber F, Hammersen B, Eick D. Ongoing mutations in the N-terminal domain of c-myc affect transactivation in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. Oncogene. 1994;9:759–763. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

