A health promotion perspective for the control and prevention of Brucellosis (Brucella melitensis); Israel as a case study
- PMID: 36155492
- PMCID: PMC9536624
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010816
A health promotion perspective for the control and prevention of Brucellosis (Brucella melitensis); Israel as a case study
Abstract
Background: Brucellosis (Brucella melitensis) is endemic in many countries around the world, therefore, identifying what is required to control and prevent the disease is essential. The health promotion concept and five areas of action, presented in the Ottawa Charter (1986) may help understand how to go forward in the prevention of the disease. Israel serves as a case study.
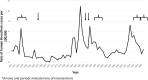
Aim: To identify barriers to the control and prevention of brucellosis (Brucella melitensis) in Israel by analyzing trends in incidence in conjunction with interventions implemented over the last seven decades, applying the health promotion areas of action.
Methods: 1. A document review approach was adopted to develop a list of interventions implemented in Israel to prevent and control brucellosis and identify barriers to implementation. These were analysed using the health promotion areas of action. 2. Data from the mandatory reporting of infectious diseases in Israel regarding brucellosis in humans between 1951 and 2021 are presented and analyzed in conjunction with the interventions implemented.
Results: A large range of interventions were implemented following outbreaks of the disease. These interventions followed the health promotion areas of action, including mainly: policy, education and environment and brought about a decrease in the disease among both animals and humans. However, major interventions were discontinued after a few years. In addition, we identified some areas of action that could be much improved on. The interventions, in many cases were not simultaneously implemented or coordinated, decreasing the chances of them having the expected long term impact.
Conclusions: Control and prevention of the disease in Israel is partial. Areas of action that could be improved include enforcement of regulations, strengthening community action and improving personal skills. Simultaneous and continuous implementation of the interventions may achieve the goals of sustained prevention and control. There seems to be a lack of a long-term strategy and an integrated holistic intervention approach that may contribute to the control and prevention of the disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
National epidemiology of culture-confirmed brucellosis in Israel, 2004-2022.Epidemiol Infect. 2024 May 21;152:e88. doi: 10.1017/S0950268824000803. Epidemiol Infect. 2024. PMID: 38770575 Free PMC article.
-
Public and animal health risks associated with spillover of Brucella melitensis into dairy farms.Microb Genom. 2023 Apr;9(4):mgen001014. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001014. Microb Genom. 2023. PMID: 37115199 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the problem of B. Melitensis and rationalizing a vaccination programme in Israel.Prilozi. 2010;31(1):167-80. Prilozi. 2010. PMID: 20703190
-
Incidence and control of brucellosis in the Near East region.Vet Microbiol. 2002 Dec 20;90(1-4):81-110. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(02)00248-1. Vet Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12414137 Review.
-
Essential role of vaccines in brucellosis control and eradication programs for livestock.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2005 Dec;4(6):915-28. doi: 10.1586/14760584.4.6.915. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2005. PMID: 16372886 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatiotemporal dynamics and influencing factors of human brucellosis in Mainland China from 2005-2021.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 11;24(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08858-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38212685 Free PMC article.
-
Long ignored but making a comeback: a worldwide epidemiological evolution of human brucellosis.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024 Dec;13(1):2290839. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2023.2290839. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 38039063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
National epidemiology of culture-confirmed brucellosis in Israel, 2004-2022.Epidemiol Infect. 2024 May 21;152:e88. doi: 10.1017/S0950268824000803. Epidemiol Infect. 2024. PMID: 38770575 Free PMC article.
-
An Epidemiological Study of Brucellosis in Different Animal Species from the Al-Qassim Region, Saudi Arabia.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Mar 17;11(3):694. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11030694. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36992277 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Multidisciplinary Rehabilitation Nursing in Patients with Brucellar Spondylitis and Its Effects on Pain, Inflammation, and Immune Function.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025 Jul 2;18:3813-3826. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S528741. eCollection 2025. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025. PMID: 40625556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou K, Wu B, Pan H, Paudyal N, Jiang J, Zhang L, et al.. ONE Health Approach to Address Zoonotic Brucellosis: A Spatiotemporal Associations Study Between Animals and Humans. Front Vet Sci [Internet]. 2020. Sep 2 [cited 2021 Apr 25];7. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fvets.2020.00521/full - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corbel M. Brucellosis in humans and animals [Internet]. WHO; 2006. [cited 2021 Apr 28]. Available from: https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=nCcGbURUDMgC&oi=fnd&pg=PR7&d...
-
- Ghanbari MK, Gorji HA, Behzadifar M, Sanee N, Mehedi N, Bragazzi NL. One health approach to tackle brucellosis: a systematic review. Trop Med Health [Internet]. 2020. Dec 20 [cited 2021 Apr 22];48(1):86. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s41182-020-00272-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources