Unique and shared systemic biomarkers for emphysema in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin deficiency and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 36155958
- PMCID: PMC9507992
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104262
Unique and shared systemic biomarkers for emphysema in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin deficiency and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
Background: Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency (AATD), the most common genetic cause of emphysema presents with unexplained phenotypic heterogeneity in affected subjects. Our objectives to identify unique and shared AATD plasma biomarkers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may explain AATD phenotypic heterogeneity.
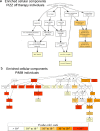
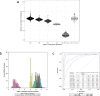
Methods: The plasma or serum of 5,924 subjects from four AATD and COPD cohorts were analyzed on SomaScan V4.0 platform. Using multivariable linear regression, inverse variance random-effects meta-analysis, and Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression we tested the association between 4,720 individual proteins or combined in a protein score with emphysema measured by 15th percentile lung density (PD15) or diffusion capacity (DLCO) in distinct AATD genotypes (Pi*ZZ, Pi*SZ, Pi*MZ) and non-AATD, PiMM COPD subjects. AAT SOMAmer accuracy for identifying AATD was tested using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis.
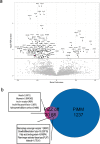
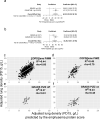
Findings: In PiZZ AATD subjects, 2 unique proteins were associated with PD15 and 98 proteins with DLCO. Of those, 68 were also associated with DLCO in COPD also and enriched for three cellular component pathways: insulin-like growth factor, lipid droplet, and myosin complex. PiMZ AATD subjects shared similar proteins associated with DLCO as COPD subjects. Our emphysema protein score included 262 SOMAmers and predicted emphysema in AATD and COPD subjects. SOMAmer AAT level <7.99 relative fluorescence unit (RFU) had 100% sensitivity and specificity for identifying Pi*ZZ, but it was lower for other AATD genotypes.
Interpretation: Using SomaScan, we identified unique and shared plasma biomarkers between AATD and COPD subjects and generated a protein score that strongly associates with emphysema in COPD and AATD. Furthermore, we discovered unique biomarkers associated with DLCO and emphysema in PiZZ AATD.
Funding: This work was supported by a grant from the Alpha-1 Foundation to RPB. COPDGene was supported by Award U01 HL089897 and U01 HL089856 from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Proteomics for COPDGene was supported by NIH 1R01HL137995. GRADS was supported by Award U01HL112707, U01 HL112695 from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, and UL1TRR002535 to CCTSI; QUANTUM-1 was supported by the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, the Office of Rare Diseases through the Rare Lung Disease Clinical Research Network (1 U54 RR019498-01, Trapnell PI), and the Alpha-1 Foundation. COPDGene is also supported by the COPD Foundation through contributions made to an Industry Advisory Board that has included AstraZeneca, Bayer Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Pfizer, and Sunovion.
Keywords: Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency; Emphysema; Plasma biomarker; Protein score; SomaScan.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests KAS serves on Alpha-1 Foundation Grant Advisory Committee, Alpha-1 Foundation Medical Advisory and Scientific Committee, ATS - RCMB Website Committee, National Jewish Health IBC committee (all unpaid); KAP does not report any potential conflict of interest; CS reports grants or contracts from Adverum, Arrowhead, AstraZeneca, CSA Medical, Grifols, Nuvaira, Takeda, Vertex; consulting fees from AstraZenca, Dicerna, Glaxo Smith Kline, Inhibrx, Morair, UpToDate, Vertex; has received honoraria for presentations from the American Thoracic Society; has received support for travel from CSL Behring; serves as the Medical Director for AlphaNet; RAS reports grants or contracts from Vertex, NIH/NCATS, Alpha-1 Foundation, consulting fees from Grifols, CSL Behring, Vertex, Intellia, Inhibrx, Takeda, Evolve Biologics, has received travel support from CSL Behring; has served on the Advisory Board of Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, and serves as the Medical Director for AlphaNet and on the board of directors for Global Implementation Solutions, Osteogenesis Imperfecta Foundation, Alpha-1 Foundation, and AlphaNet; AMT reports grants or contracts from Vertex, Grifols, and CSl Behring; has received consulting fees from CSL Behring, Inhibrix, Z-factor, and Takeda, has received honoraria for lectures from Glaxo Smith Kline and AstraZeneca; TB does not report any potential conflict of interest; DAS does not report any potential conflict of interest; LM does not report any potential conflict of interest; NH does not report any potential conflict of interest; EKS reports grants or contracts from Glaxo Smith Kline, Bayer; BDH does not report any potential conflict of interest; CPH reports grants or contracts from Alpha-1 Foundation, Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, and Vertex, consulting fees from AstraZeneca and Takeda; DLD has received honoraria for lectures from Novartis and financial support from Bayer towards the institution; MHC reports grants or contracts from Glaxo Smith Kline, Bayer, consulting fees from AstraZeneca and Genentech, honoraria for presentations from Illumina, RPB does not report any potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Silverman EK, Sandhaus RA. Clinical practice. Alpha1-Antitrypsin deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(26):2749–2757. - PubMed
-
- Blanco I, de Serres FJ, Fernandez-Bustillo E, Lara B, Miravitlles M. Estimated numbers and prevalence of Pi*S and Pi*Z alleles of alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency in European countries. Eur Respir J. 2006;27(1):77–84. - PubMed
-
- Dahl M, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Lange P, Vestbo J, Nordestgaard BG. Change in lung function and morbidity from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in alpha1-antitrypsin MZ heterozygotes: a longitudinal study of the general population. Ann Intern Med. 2002;136(4):270–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

