Rapid artificial intelligence solutions in a pandemic-The COVID-19-20 Lung CT Lesion Segmentation Challenge
- PMID: 36156419
- PMCID: PMC9444848
- DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102605
Rapid artificial intelligence solutions in a pandemic-The COVID-19-20 Lung CT Lesion Segmentation Challenge
Abstract
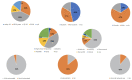
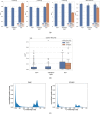
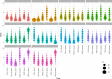
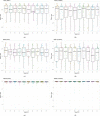
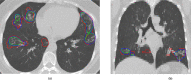
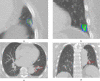
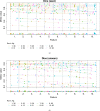
Artificial intelligence (AI) methods for the automatic detection and quantification of COVID-19 lesions in chest computed tomography (CT) might play an important role in the monitoring and management of the disease. We organized an international challenge and competition for the development and comparison of AI algorithms for this task, which we supported with public data and state-of-the-art benchmark methods. Board Certified Radiologists annotated 295 public images from two sources (A and B) for algorithms training (n=199, source A), validation (n=50, source A) and testing (n=23, source A; n=23, source B). There were 1,096 registered teams of which 225 and 98 completed the validation and testing phases, respectively. The challenge showed that AI models could be rapidly designed by diverse teams with the potential to measure disease or facilitate timely and patient-specific interventions. This paper provides an overview and the major outcomes of the COVID-19 Lung CT Lesion Segmentation Challenge - 2020.
Keywords: COVID-19; Challenge; Medical image segmentation.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Update of
-
Rapid Artificial Intelligence Solutions in a Pandemic - The COVID-19-20 Lung CT Lesion Segmentation Challenge.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2021 Jun 4:rs.3.rs-571332. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-571332/v1. Res Sq. 2021. Update in: Med Image Anal. 2022 Nov;82:102605. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102605. PMID: 34100010 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bai Harrison X, Wang Robin, Xiong Zeng, Hsieh Ben, Chang Ken, Halsey Kasey, Tran Thi My Linh, Choi Ji Whae, Wang Dong-Cui, Shi Lin-Bo, et al. Artificial intelligence augmentation of radiologist performance in distinguishing COVID-19 from pneumonia of other origin at chest CT. Radiology. 2020;296(3):E156–E165. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

