Bone Safety Profile of Steroidal Aromatase Inhibitor in Comparison to Nonsteroidal Aromatase Inhibitors in Postmenopausal Women with Breast Cancer: A Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36156912
- PMCID: PMC9453661
- DOI: 10.1159/000523695
Bone Safety Profile of Steroidal Aromatase Inhibitor in Comparison to Nonsteroidal Aromatase Inhibitors in Postmenopausal Women with Breast Cancer: A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background and objectives: Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) provide an alternative to tamoxifen as an adjuvant therapy for postmenopausal patients with breast cancer (BC). Large trials resulted better outcomes with AIs. Adjuvant therapy with AIs reduced the risk of relapse compared with tamoxifen. Systemic therapies for BC can interfere with bone turnover, either by affecting gonadal steroid hormone production or by inhibiting peripheral aromatization into estrogen. We aimed to evaluate the safety profile of bone-related events by comparing 3 AIs with tamoxifen and a placebo.
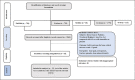
Methods: The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines were used for network meta-analyses (NMAs). Searches were performed using PubMed, Embase/Medline, Cochrane, and Ovid databases. Randomized controlled trials comparing tamoxifen and placebo or other AIs to steroidal or nonsteroidal AIs in patients with BC reporting bone-related safety events were included in NMA. NMA in a Bayesian approach was performed using R software (ver 3.2), Gemtc package.
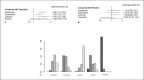
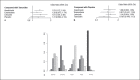
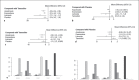
Results: Seventeen studies reporting 4 different bone-related endpoints were included. Although there was no statistical significance, treatment with exemestane lowered the incidence of bone pain (odds ratio [OR] vs. anastrozole and letrozole: 0.63, 0.54), fracture episodes (OR vs. anastrozole and letrozole: 0.84, 0.80), and osteoporosis (OR vs. anastrozole and letrozole: 0.85, 0.73) compared with letrozole and anastrozole. Reduction in bone mineral density was lesser in exemestane than in anastrozole (mean reduction in hip: 1.05; lumbar spine: 1.25). Treatment ranking with the surface under the cumulative ranking curve showed that exemestane was found to reduce the incidence of bone-related adverse events.
Conclusion: A lower incidence of bone-related safety events was observed in patients treated with exemestane.
Keywords: Aromatase inhibitor; Bone; Exemestane; Meta-analysis; Network; Tamoxifen.
Copyright © 2022 by The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Are all aromatase inhibitors the same? A review of controlled clinical trials in breast cancer.Clin Ther. 2005 Nov;27(11):1671-84. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.11.013. Clin Ther. 2005. PMID: 16368441 Review.
-
Comparative study on individual aromatase inhibitors on cardiovascular safety profile: a network meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Sep 29;8:2721-30. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S88179. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 26491345 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular safety profiles of aromatase inhibitors : a comparative review.Drug Saf. 2006;29(9):785-801. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200629090-00003. Drug Saf. 2006. PMID: 16944964 Review.
-
Emerging role of aromatase inhibitors in the adjuvant setting.Am J Clin Oncol. 2003 Aug;26(4):S27-33. doi: 10.1097/00000421-200308001-00005. Am J Clin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12902874 Review.
-
The role of aromatase inhibitors in early breast cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2003 Apr;4(2):133-40. doi: 10.1007/s11864-003-0014-y. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12594939 Review.
Cited by
-
The recent progress of endocrine therapy-induced osteoporosis in estrogen-positive breast cancer therapy.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 7;13:1218206. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1218206. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37483519 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68((6)):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Tomao F, Spinelli G, Vici P, Pisanelli GC, Cascialli G, Frati L, et al. Current role and safety profile of aromatase inhibitors in early breast cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011 Aug;11((8)):1253–63. - PubMed
-
- Smith IE, Dowsett M, Ebbs SR, Dixon JM, Skene A, Blohmer J-U, et al. Neoadjuvant treatment of postmenopausal breast cancer with anastrozole, tamoxifen, or both in combination: the Immediate Preoperative Anastrozole, Tamoxifen, or Combined with Tamoxifen (IMPACT) multicenter double-blind randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2005 Aug;23((22)):5108–16. - PubMed
-
- Cataliotti L, Buzdar AU, Noguchi S, Bines J, Takatsuka Y, Petrakova K, et al. Comparison of anastrozole versus tamoxifen as preoperative therapy in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: the pre-operative “arimidex” compared to tamoxifen (PROACT) trial. Cancer. 2006 May;106((10)):2095–103. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

