OEA loaded liposomes with the neuroprotective effect for stroke therapy
- PMID: 36157031
- PMCID: PMC9493034
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1014208
OEA loaded liposomes with the neuroprotective effect for stroke therapy
Abstract
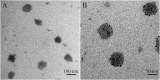
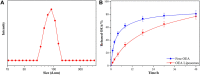
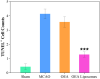
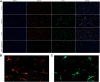
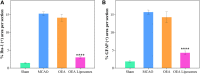
With high mortality, stroke has become a serious threat to human health. Nevertheless, the strategy for stroke therapy is quite limited in the clinic till now. In this research, we prepared a novel neuroprotective nanoformulation (OEA Liposomes) via encapsulating endogenous N-oleoylethanolamine (OEA) in liposomes for intravenous administration. The formulation largely increased the solubility and bioavailability of OEA. Then the following systematic experiments stated the excellent neuroprotective effect of OEA Liposomes in vivo. The survival rate of the nanodrug group was largely increased to 75%, while that of the Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion (MCAO) group was only 41.7%. And the severe neurological functional deficit of the MCAO rats was also significantly improved. What's more, the OEA Liposomes could inhibit the apoptosis of neurons and the inflammation of reperfusion to a very slight level, indicating their outstanding neuroprotective effect. These results indicated that the OEA Liposomes have a great potential for clinic anti-stroke application.
Keywords: OEA; drug delivery; ischemia reperfusion; neurprotective effect; stroke.
Copyright © 2022 Wu and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integration of phospholipid-complex nanocarrier assembly with endogenous N-oleoylethanolamine for efficient stroke therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2019 Jan 19;17(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12951-019-0442-x. J Nanobiotechnology. 2019. PMID: 30660200 Free PMC article.
-
N-oleoylethanolamine - phosphatidylcholine complex loaded, DSPE-PEG integrated liposomes for efficient stroke.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):2525-2533. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.2008058. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 34842016 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous Oleoylethanolamide Crystals Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles with Enhanced Hydrophobic Drug Loading Capacity for Efficient Stroke Therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Dec 21;16:8103-8115. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S344318. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34992362 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective profile of enoxaparin, a low molecular weight heparin, in in vivo models of cerebral ischemia or traumatic brain injury in rats: a review.CNS Drug Rev. 2002 Spring;8(1):1-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2002.tb00213.x. CNS Drug Rev. 2002. PMID: 12070524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nasal Delivery of Antioxidants by Cholesterol-incorporated Liposomes Extends the Neuroprotective Time Window in Cerebral Ischemia.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(40):6223-6230. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170825124515. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28847301 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological potential of endocannabinoid and endocannabinoid-like compounds in protecting intestinal structure and metabolism under high-fat conditions.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 22;16:1567543. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1567543. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40474970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revolutionizing Stroke Care: Nanotechnology-Based Brain Delivery as a Novel Paradigm for Treatment and Diagnosis.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jan;62(1):184-220. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04215-3. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 38829514 Review.
References
-
- Ansari M., Eslami H., Javadpour S., Yousefi E. (2021). Cancer therapy using a targeted magnetoliposomes encapsulated doxorubicin assisted ultrasound. Mater. Technol. 37, 858–865. 10.1080/10667857.2021.1903136 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

