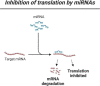
Precision machine learning to understand micro-RNA regulation in neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 36157078
- PMCID: PMC9500540
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.914830
Precision machine learning to understand micro-RNA regulation in neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
Micro-RNAs (miRNAs) are short (∼21 nt) non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression through the degradation or translational repression of mRNAs. Accumulating evidence points to a role of miRNA regulation in the pathogenesis of a wide range of neurodegenerative (ND) diseases such as, for example, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Huntington disease (HD). Several systems level studies aimed to explore the role of miRNA regulation in NDs, but these studies remain challenging. Part of the problem may be related to the lack of sufficiently rich or homogeneous data, such as time series or cell-type-specific data obtained in model systems or human biosamples, to account for context dependency. Part of the problem may also be related to the methodological challenges associated with the accurate system-level modeling of miRNA and mRNA data. Here, we critically review the main families of machine learning methods used to analyze expression data, highlighting the added value of using shape-analysis concepts as a solution for precisely modeling highly dimensional miRNA and mRNA data such as the ones obtained in the study of the HD process, and elaborating on the potential of these concepts and methods for modeling complex omics data.
Keywords: complex RNA-seq data; machine learning; miRNA regulation; neurodegenerative disease; precision analysis; shape analysis.
Copyright © 2022 Mégret, Mendoza, Arrieta Lobo, Brouillet, Nguyen, Bouaziz, Chambaz and Néri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combining feature selection and shape analysis uncovers precise rules for miRNA regulation in Huntington's disease mice.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Feb 24;21(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-3418-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32093602 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of MitomiRs in the Pathophysiology of Human Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;888:123-54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22671-2_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26663182
-
Long Non-coding RNAs in Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 30;9:719247. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.719247. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34527672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNAs and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;888:85-105. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22671-2_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26663180 Review.
-
Roles of long noncoding RNAs in brain development, functional diversification and neurodegenerative diseases.Brain Res Bull. 2013 Aug;97:69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23756188 Review.
Cited by
-
Advancing miRNA cancer research through artificial intelligence: from biomarker discovery to therapeutic targeting.Med Oncol. 2024 Dec 17;42(1):30. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02579-z. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39688780 Review.
-
Proteomics profiling and machine learning in nusinersen-treated patients with spinal muscular atrophy.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Sep 10;81(1):393. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05426-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39254732 Free PMC article.
-
DMGAT: predicting ncRNA-drug resistance associations based on diffusion map and heterogeneous graph attention network.Brief Bioinform. 2025 Mar 4;26(2):bbaf179. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaf179. Brief Bioinform. 2025. PMID: 40251829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman N. S. (1992). An Introduction to Kernel and Nearest-Neighbor Nonparametric Regression. Am. Statistician 46 175–185. 10.1080/00031305.1992.10475879 - DOI
-
- Berger J. O., Moreno E., Pericchi L. R., Bayarri M. J., Bernardo J. M., Cano J. A., et al. (1994). An overview of robust Bayesian analysis. Test 3 5–124. 10.1007/BF02562676 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials