PK/PD integration of florfenicol alone and in combination with doxycycline against Riemerella anatipestifer
- PMID: 36157174
- PMCID: PMC9493122
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.975673
PK/PD integration of florfenicol alone and in combination with doxycycline against Riemerella anatipestifer
Abstract
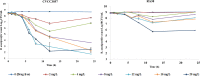
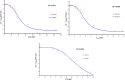
Riemerella anatipestifer (RA) is an important pathogen found in poultry. RA infection can kill ducks and lead to significant economic losses. Seven RA strains with different susceptibility phenotypes were chosen to study the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) integration of florfenicol (FF) alone and in combination with doxycycline (DOX). The checkerboard assay indicated that synergy [fractional inhibitory concentration index (FICI) ≤ 0.5] was detected in the CVCC3952 strain of RA and that additivity (FICI >0.5 to ≤ 1) was observed in other strains. Static time-kill curves showed that the bactericidal effect of FF against RA was produced at a FF concentration ≥4 MIC, and the antibacterial activity of FF against RA was enhanced from the aspects of efficacy and efficacy in combination with DOX. Dynamic time-kill curves indicated that FF elicited bactericidal activity against the CVCC3857 strain with a reduction ≥4.88 log10CFU/ml when the dose was ≥8 mg/L. However, a bactericidal effect was not achieved at the maximum administered dose of FF monotherapy (20 mg/L) for isolates with a MIC ≥4 μg/ml. The effect of FF against RA was enhanced upon combination with DOX. The combination of FF with DOX reduced the bacterial burden ≥4.53 log10CFU/ml for all strains with a MIC ≥4 μg/ml. Data were fitted to a sigmoidal Emax model. The PK/PD parameters of AUC24h/MIC (the area under the concentration-time curve over 24 h divided by the MIC) and %T >MIC (the cumulative percentage of time over a 24-h period at which the concentration exceeded the MIC) of FF for eliciting a reduction of 3 log10CFU/ml was 40.10 h and 58.71, respectively. For strains with a MIC ≤ 16 μg/ml, the magnitude of the AUC24h/MIC and Cmax/MIC required for a 3 log10CFU/ml of bacterial killing was 34.84 h and 4.74 in the presence of DOX at 0.5 MIC, respectively. These data suggest that combination of FF with DOX enhanced the activity against RA strains with various susceptibilities to FF and DOX.
Keywords: PK/PD model; Riemerella anatipestifer; combination therapy; doxycycline; florfenicol.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Huang, Yu, Liu and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
PK-PD integration of enrofloxacin and cefquinome alone and in combination against Klebsiella pneumoniae using an in vitro dynamic model.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 6;14:1226936. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1226936. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37869750 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study and cutoff of florfenicol against Riemerella anatipestifer in ducks.Poult Sci. 2025 Jan;104(1):104635. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104635. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39647361 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship of florfenicol in combination with doxycycline against Riemerella anatipestifer in ducks and the effect upon resistance development.Poult Sci. 2025 Apr;104(4):104922. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104922. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39985898 Free PMC article.
-
The dose regimen formulation of tilmicosin against Lawsonia intracellularis in pigs by pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) model.Microb Pathog. 2020 Oct;147:104389. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104389. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32707311 Review.
-
How can we predict bacterial eradication?Int J Infect Dis. 2003 Mar;7 Suppl 1:S13-20. doi: 10.1016/s1201-9712(03)90066-x. Int J Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12839703 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Riemerella anatipestifer infection in chickens: pathogenic characteristics and host immune response profiles.Poult Sci. 2025 Aug 14;104(11):105687. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105687. Online ahead of print. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40840279 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic integration of tilmicosin against Pasteurella multocida in a piglet tissue cage model.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Sep 4;10:1260990. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1260990. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37732140 Free PMC article.
-
PK-PD integration of enrofloxacin and cefquinome alone and in combination against Klebsiella pneumoniae using an in vitro dynamic model.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 6;14:1226936. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1226936. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37869750 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study and cutoff of florfenicol against Riemerella anatipestifer in ducks.Poult Sci. 2025 Jan;104(1):104635. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104635. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39647361 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship of florfenicol in combination with doxycycline against Riemerella anatipestifer in ducks and the effect upon resistance development.Poult Sci. 2025 Apr;104(4):104922. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104922. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39985898 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

