Value of Cytokine Expression in Early Diagnosis and Prognosis of Tumor Metastasis
- PMID: 36157224
- PMCID: PMC9507706
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8112190
Value of Cytokine Expression in Early Diagnosis and Prognosis of Tumor Metastasis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the association of the plasma level of cytokines and blood routine indexes with clinical characteristics in patients with cancer.
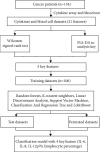
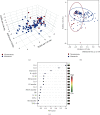
Methods: We analyzed plasma samples derived from 134 cancer patients. Interleukins (IL) 1β, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12p70, 17, IFN-γ, IFN-α, and TNF-α, and blood routine indexes were measured. The associations of the levels of cytokine and blood routine indexes with demographic and clinical characteristics of cancer patients were analyzed. Partial least-squares discriminant analysis was employed to identify cancer metastasis using these plasma cytokine metrics as input. We compared the predictive effectiveness of numeric machine learning algorithms using these indexes and showed a promising model implemented with random forest.
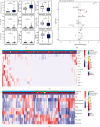
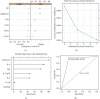
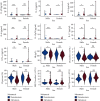
Results: Plasma levels of IL-6 and IL-8 in cancer patients with metastases were higher than those without metastases (P < 0.05). Cancer patients without metastases had significantly higher levels of plasma IL-12p70 and percentage of lymphocytes as compared with those with metastases (P < 0.05). Our random forest model showed the highest prediction performance (upper quantile AUC, 0.885) among the six machine learning algorithms we evaluated.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that plasma levels of IL-6, IL-8, and IL-12p70 and the percentage of lymphocytes could predict the recurrence, metastasis, and progression of cancer. Our findings will provide guidance for tumor monitoring and treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Tingwei Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hulvat M. C. Cancer incidence and trends. Surgical Clinics of North America . 2020;100:469–481. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

