Chronic Kidney Disease and Cognitive Impairment: The Kidney-Brain Axis
- PMID: 36157262
- PMCID: PMC9386403
- DOI: 10.1159/000524475
Chronic Kidney Disease and Cognitive Impairment: The Kidney-Brain Axis
Abstract
Background: Cognitive impairment, increasingly recognized as a major social burden, is commonly found in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients.
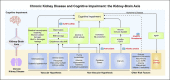
Summary: Vascular damage, uremic toxicity, oxidative stress, and peripheral/central inflammation induced by CKD might be involved in brain lesions and ultimately result in cognitive decline. Uncovering the pathophysiology of CKD-associated cognitive impairment is important for early diagnosis and prevention, which undoubtedly prompts innovative pharmacological treatments.
Key messages: Here, we sequentially review the current understanding and advances in the epidemiology, risk factors, and pathological mechanisms of cognitive impairment in CKD. Furthermore, we summarize the currently available therapeutic strategies for cognitive impairment in CKD.
Keywords: Cognitive impairment; Kidney-brain axis; Mechanism; Treatment.
Copyright © 2022 by The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Kalantar-Zadeh K, Jafar TH, Nitsch D, Neuen BL, Perkovic V. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2021 Aug 28;398((10302)):786–802. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

