Discovery of the First Lytic Staphylococcus pseudintermedius/ Staphylococcus aureus Polyvalent Bacteriophages
- PMID: 36157281
- PMCID: PMC9248872
- DOI: 10.1089/phage.2022.0004
Discovery of the First Lytic Staphylococcus pseudintermedius/ Staphylococcus aureus Polyvalent Bacteriophages
Abstract
Background: There are no verified lytic Staphylococcus pseudintermedius phages in the literature and few temperate phage genomes in databases. S. pseudintermedius is an opportunistic zoonotic pathogen of great importance in veterinary and human medicine.
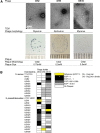
Materials and methods: We discovered phages against canine-derived S. pseudintermedius isolates by screening dog feces, hair, and skin swabs. Fourteen new phages were isolated and characterized by genomic analysis, transmission electron microscopy, and host range determination.
Results: Three phages-DH2, DH5, and DS10, a phage K variant-were predicted lytic by sequencing, a designation supported by mitomycin C induction. All three are S. pseudintermedius and Staphylococcus aureus polyvalent phages, with DH2 and DS10 being strong killers of both species.
Conclusions: We report discovery of the first verified lytic S. pseudintermedius phages and suggest dog hair as a novel reservoir. DH2, DH5, and DS10 are promising candidates toward developing an anti-Staphylococcal phage cocktail.
Keywords: canine; lytic; pseudintermedius; pyoderma; virulent.
Copyright 2022, Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages active against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius.Res Vet Sci. 2019 Feb;122:81-85. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2018.11.008. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Res Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 30468880
-
Analysis host-recognition mechanism of staphylococcal kayvirus ɸSA039 reveals a novel strategy that protects Staphylococcus aureus against infection by Staphylococcus pseudintermedius Siphoviridae phages.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Aug;103(16):6809-6823. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09940-7. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31236618
-
Lytic Activity of Polyvalent Staphylococcal Bacteriophage PhiSA012 and Its Endolysin Lys-PhiSA012 Against Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcal Clinical Isolates From Canine Skin Infection Sites.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Jun 10;7:234. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00234. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32587860 Free PMC article.
-
Human Colonization and Infection by Staphylococcus pseudintermedius: An Emerging and Underestimated Zoonotic Pathogen.Microorganisms. 2023 Feb 25;11(3):581. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030581. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36985155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Not just in man's best friend: A review of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius host range and human zoonosis.Res Vet Sci. 2024 Jul;174:105305. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2024.105305. Epub 2024 May 14. Res Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38805894 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Strategies Proposed for the Treatment of S. pseudintermedius and Other Dermato-Pathogenic Staphylococcus spp. in Companion Animals: A Narrative Review.Vet Sci. 2024 Jul 11;11(7):311. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11070311. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39057995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topical Bacteriophage Therapy for Staphylococcal Superficial Pyoderma in Horses: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study.Pathogens. 2023 Jun 14;12(6):828. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12060828. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37375518 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius: epidemiological changes, antibiotic resistance, and alternative therapeutic strategies.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Dec;48(6):3505-3515. doi: 10.1007/s11259-024-10508-8. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 39167258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successful phage-antibiotic therapy of P. aeruginosa implant-associated infection in a Siamese cat.Vet Q. 2024 Dec;44(1):1-9. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2024.2350661. Epub 2024 May 10. Vet Q. 2024. PMID: 38726795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ross Fitzgerald J. The Staphylococcus intermedius group of bacterial pathogens: Species re-classification, pathogenesis and the emergence of meticillin resistance: Recent studies of the staphylococcus intermedius group. Vet Dermatol 2009;20(5–6):490–495; doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3164.2009.00828.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
