Use of the European standardization framework established by CEN/TC 216 for effective disinfection strategies in human medicine, veterinary medicine, food hygiene, industry, and domestic and institutional use - a review
- PMID: 36157383
- PMCID: PMC9487781
- DOI: 10.3205/dgkh000417
Use of the European standardization framework established by CEN/TC 216 for effective disinfection strategies in human medicine, veterinary medicine, food hygiene, industry, and domestic and institutional use - a review
Abstract
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic illustrates the necessity of effective preventive measures for existing and newly emerging pathogens. When confronted with pathogens or spoilage agents, especially if they are not yet well studied, effective hygiene protocols are needed immediately. In the medical field, effective preventive measures are key to prevent vulnerable patients from infections. In production areas, effective hygiene measures are needed to protect goods from spoilage or microbial contamination. The European standardization framework established by the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) ensures that effective hygiene measures are available and can be immediately implemented when needed. Based on a broad portfolio of standards/laboratory tests, activity claims specifically addressing the special features of applications of antimicrobial formulations are substantiated. In this review, the concept of using standardized surrogate test organisms is explained, and the European standardized test approach to claim microbicidal and virucidal efficacy, the specificity of claims and their relevance for infection prevention measures is illustrated. Furthermore, relevance of the European Norm test methods is elucidated in the light of legal requirements. Finally, the review explains the systematics of the standardized methodological portfolio of CEN, Technical Committee 216, which is very useful when effective strategies for fighting or preventing microbial and viral induced infections, contaminations or spoilage are needed on an immediate basis.
Die SARS-CoV-2-Pandemie verdeutlicht die Notwendigkeit wirksamer Präventionsmaßnahmen für bekannte und neu auftretende Krankheitserreger. Wenn man mit Krankheits- oder Verderbniserregern konfrontiert wird, insbesondere wenn sie noch nicht gut erforscht sind, sind sofort wirksame Hygieneprotokolle erforderlich. Im medizinischen Bereich sind wirksame Präventionsmaßnahmen von entscheidender Bedeutung, um efährdete Patienten vor Infektionen zu schützen. Ebenso sind in Produktionsbereichen wirksame Hygienemaßnahmen erforderlich, um Waren vor Verderb oder mikrobieller Verunreinigung zu bewahren. Mit Hilfe der vom Europäischen Komitee für Normung (CEN) erarbeiteten Normen im Bereich der Desinfektion und Antisepsis können wirksame Hygienemaßnahmen kurzfristig und bedarfsgerecht etabliert werden. Auf der Grundlage eines breiten Portfolios von Normen/Labortests werden Wirksamkeitsauslobungen begründet, die speziell die Besonderheiten bei der Anwendung mikrobizider Formulierungen im Fokus haben. In der Übersichtsarbeit wird das Konzept der Verwendung standardisierter Surrogat-Testorganismen erläutert und das standardisierte europäische Methodenportfolio zur Auslobung der mikrobiziden und viruzider Wirksamkeit, die Spezifität der Auslobung und ihre Relevanz für Maßnahmen zur Infektionsprävention veranschaulicht sowie die Relevanz der Testmethoden der Europäischen Normen im Hinblick auf die gesetzlichen Anforderungen erläutert. Abschließend wird die Systematik des standardisierten Methodenportfolios des Technischen Komitees 216 des CEN erläutert, das von großem Nutzen ist, wenn wirksame Strategien zur Bekämpfung oder Verhinderung von mikrobiell oder viral bedingten Infektionen, Kontaminationen oder Verderb unmittelbar erforderlich sind.
Keywords: EN 14885; disinfection; food; human medicine; industry; microbicidal efficacy; norms; veterinary medicine; virucidal efficacy.
Copyright © 2022 Bolten et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Author AB is an employee of Bode Chemie GmbH, Hamburg, Germany. Author VS is an employee of Chemische Fabrik Dr. Weigert GmbH & Co. KG, Hamburg, Germany. Author KS is an employee of bactologicum GmbH, Itzehoe, Germany, and formerly was an employee of Schülke & Mayr GmbH, Norderstedt, Germany.
Figures

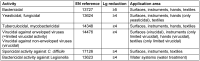






References
-
- Hui DS, I Azhar E, Madani TA, Ntoumi F, Kock R, Dar O, Ippolito G, Mchugh TD, Memish ZA, Drosten C, Zumla A, Petersen E. The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health – The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Feb;91:264–266. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) IInfection prevention and control during health care when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected. Interim guidance. 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-HCF_assessment-IPC....
-
- Robert Koch-Institut (RKI) Empfehlungen des RKI für die Hygienemaßnahmen und Infektionskontrolle bei Patienten mit Pneumonien verursacht durch ein neuartiges Coronavirus (nCoV) aus Wuhan, China. 2020. [Accessed 2021 Dec 23]. Available from: https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/InfAZ/N/Neuartiges_Coronavirus/Hygiene.htm....
-
- Robert Koch-Institut (RKI) Empfehlungen des Robert Koch-Institutes für die Hygienemaßnahmen und Infektionskontrolle bei Patienten mit Schwerem Akutem Respiratorischem Syndrom (SARS) 2015. [Accessed 2021 Dec 23]. Available from: https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/Infekt/Krankenhaushygiene/Erreger_ausgewae....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

