Traction-bed-assisted reduction and double-plate fixation for treatment of comminuted femoral intertrochanteric fractures with coronal split
- PMID: 36157415
- PMCID: PMC9500341
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.984431
Traction-bed-assisted reduction and double-plate fixation for treatment of comminuted femoral intertrochanteric fractures with coronal split
Abstract
Background: A coronal comminuted femoral intertrochanteric fracture is a special type of fracture that easily leads to internal fixation failure, and the current internal fixation techniques remain controversial. This study aims to evaluate the effect of traction-bed-assisted reduction and double-plate internal fixation in the treatment of comminuted and coronally split intertrochanteric femoral fracture.
Method: Retrospective analyses of the clinical data of 83 patients diagnosed with, and treated for, comminuted and coronally split intertrochanteric femoral fracture from December 2017 to November 2019 were conducted. Among the total number of 83 patients, 40 patients received traction-bed-assisted reduction and PFNA fixation (the control group), whereas 43 patients received traction-bed-assisted reduction and double-plate internal fixation (the experimental group). The major indicators for the research analysis such as the general information of patients, perioperative data, and follow-up data of both groups were collected, sorted out, and meticulously analyzed.
Results: The time taken for traction-bed-assisted reduction and double-plate intern fixation in the experimental group was significantly shorter than that in the control group (P < .05). The post-operative Harris Hip Score (HHS) at 3 months and at the final follow-up after the surgery was significantly better in the experimental group compared with that in the control group, both of which were statistically significant (P < .05). However, there were statistically no significant differences between the two groups in terms of preoperative hemoglobin (Hb) level, amount of intraoperative total blood loss, immediate post-operative Hb level, incidence of wound infection within 14 days post-operatively, time taken to step up on the ground after surgery, HHS 2 weeks after surgery, time taken for fracture healing, and the incidence of complications (P > .05).
Conclusion: The use of a traction bed to achieve adequate reduction, followed by internal fixation using double plates, comparatively takes less time for both reduction and operation in the treatment of comminuted and coronally split intertrochanteric femoral fractures, which also restores proper hip joint movements relatively early and hence provides better hip joint functions in the long run.
Keywords: coronal fracture; femoral; internal fixation; intertrochanteric fracture; nonunion.
© 2022 Hu, Xie, Wang, Mi, Xue, Lin, Xiong, Hu, Zhou, Cao and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
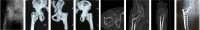
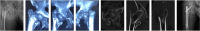




Similar articles
-
[Comparison of proximal femoral nail anti-rotation operation in traction bed supine position and non-traction bed lateral position in treatment of intertrochanteric fracture of femur].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Jan 15;34(1):32-36. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201905076. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 31939231 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[PFNA combined reconstruction and locking titanium plate for the treatment of comminuted femoral intertrochanteric fractures involving lateral wall].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2018 Sep 25;31(9):840-845. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2018.09.012. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2018. PMID: 30332878 Chinese.
-
[Effectiveness comparison between proximal femoral nail anti-rotation and proximal femoral locking compression plate for intertrochanteric fracture in elderly patients combined with hemiplegia due to cerebral infarction].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Nov 15;32(11):1411-1416. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201805073. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30417616 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Fractures of the femoral neck: a review and personal statement.Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2006;73(1):45-59. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2006. PMID: 16613748 Review.
-
Pre-Operative Traction in Femoral Fractures for Pain Management: A Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2024;12(10):683-689. doi: 10.22038/ABJS.2024.78869.3622. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2024. PMID: 39478844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

