Keyhole supraorbital eyebrow approach for fully endoscopic resection of tuberculum sellae meningioma
- PMID: 36157417
- PMCID: PMC9491022
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.971063
Keyhole supraorbital eyebrow approach for fully endoscopic resection of tuberculum sellae meningioma
Abstract
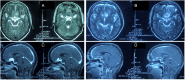
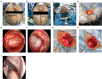
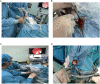
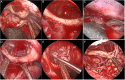
Background: The fully endoscopic supraorbital trans-eyebrow keyhole approach is a technique utilized for the transcranial resection of tuberculum sellae meningioma (TSM). Surgery is the first choice for TSM treatment. This study aimed to summarize and analyze the safety, feasibility, limitations, and technical requirements of the fully endoscopic supraorbital trans-eyebrow keyhole approach for TSM resection.
Methods: Data of 19 TSM fully endoscopic supraorbital trans-eyebrow keyhole approach resections cases (six and 13 on the left and right eyebrows, respectively) were retrospectively analyzed at the Neurosurgery Department of the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College (Bengbu, China) from August 2015 to March 2022.
Results: All 19 patients were diagnosed with meningioma (World Health Organization grade I), and according to the scope of tumor resection (EOR), 18 patients (94.7%) had gross total resection (GTR), and one patient (5.3%) had near-total resection (NTR). Preoperative chief complaints were symptomatic visual dysfunction (n = 12), headache and dizziness (n = 6), and accidental discovery (n = 1). Postoperative visual function improved in 83.3% of cases (10/12), and headache and dizziness were relieved in 83.3% of cases (5/6 patients). Postoperative intracranial infection occurred in one case and was cured by external drainage of the lumbar cistern and anti-infective treatment. Two cases of frontal lobe injury were discharged after conservative treatment. There was no postoperative olfactory dysfunction, eyelid ptosis, cerebrospinal fluid leakage, or death. There were no reports of disease recurrence or death during the 3-month follow-up at an outpatient clinic or by telephone.
Conclusion: Fully endoscopic TSM resection through the keyhole approach is safe and feasible. It can be used to explore angles that cannot be seen under a microscope and show the true value of endoscopy technology. The endoscopic equipment and technical skills of the surgeon and surgical team are important in this technique.
Keywords: endoscope; endoscopic resection; keyhole supraorbital eyebrow approach; transcranial resection; tuberculum sellae meningioma.
© 2022 Zheng, Shao, Li, Cai, Xie, Sun and Zhiquan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Keyhole supraorbital eyebrow approach for the resection of a tuberculum sellae meningioma with intraoperative endoscopic assistance.Surg Neurol Int. 2022 Mar 18;13:93. doi: 10.25259/SNI_1173_2021. eCollection 2022. Surg Neurol Int. 2022. PMID: 35399897 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscope-assisted endonasal versus supraorbital keyhole resection of olfactory groove meningiomas: comparison and combination of 2 minimally invasive approaches.J Neurosurg. 2016 Mar;124(3):605-20. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.JNS141884. Epub 2015 Aug 14. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26274992
-
Endoscopic Supraorbital Eyebrow Approach for Medium-Sized Tuberculum Sellae Meningiomas: A Cadaveric Stepwise Dissection, Technical Nuances, and Surgical Outcomes.World Neurosurg. 2023 Aug;176:e40-e48. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2023.03.063. Epub 2023 Mar 20. World Neurosurg. 2023. PMID: 36940807
-
Eyebrow supraorbital keyhole craniotomy for olfactory groove meningiomas with endoscope assistance: case series and systematic review of extent of resection, quantification of postoperative frontal lobe injury, anosmia, and recurrence.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021 Jan;163(1):101-112. doi: 10.1007/s00701-020-04552-x. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021. PMID: 32888076
-
The supraorbital endoscopic approach for tumors.World Neurosurg. 2014 Jul-Aug;82(1-2):e243-56. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2013.02.002. Epub 2013 Feb 5. World Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 23395805 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

