Effects of scoparone on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease revealed by RNA sequencing
- PMID: 36157436
- PMCID: PMC9500212
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1004284
Effects of scoparone on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease revealed by RNA sequencing
Abstract
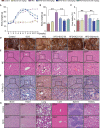
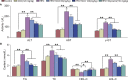
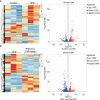
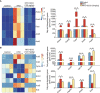
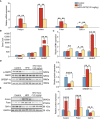
Scoparone (SCO) is known to have curative effect of alleviating liver injury. The purpose of this study was to observe the therapeutic effect and possible mechanism of SCO against high-fat diet (HFD) induced non-alcoholic liver disease (NAFLD) through in vivo experiments and RNA sequencing. Male Kunming mice were fed with HFD for 8 weeks to establish a mouse model of NAFLD, and SCO was used to treat NAFLD. Histopathology and biochemical indicators were used to evaluate the liver injury and the efficacy of SCO. RNA sequencing analysis was performed to elucidate the hepatoprotective mechanism of SCO. Finally, the differentially expressed genes of cholesterol synthesis and fatty acid (triglyceride) synthesis pathways were verified by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blot. The histopathological results showed that HFD could lead to significant steatosis in mice, while SCO could alleviate liver steatosis remarkably in NAFLD mice. The determination of biochemical indicators showed that SCO could inhibit the increased serum transaminase activity and liver lipid level induced by HFD. RNA sequencing analysis of liver tissues found that 2742 and 3663 genes were significantly changed by HFD and SCO, respectively. SCO reversed the most of genes involved in cholesterol synthesis and fatty acid (triglyceride) metabolism induced by HFD. the results of the validation experiment were mostly consistent with the RNA sequencing. SCO alleviated liver injury and steatosis in NAFLD mice, which may be closely related to the regulation of cholesterol and fatty acid (triglyceride) metabolism.
Keywords: cholesterol metabolism; fatty acid (triglyceride) metabolism; non-alcoholic liver disease (NAFLD); ribonucleic Acid (RNA) sequencing; scoparone.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Gao, Cao, Li, Mo, Li, Wu, Guo, Wei and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effects of scoparone on alcohol and high-fat diet-induced liver injury revealed by RNA sequencing.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Nov;155:113770. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113770. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36182737
-
The effects of Gentiana dahurica Fisch on alcoholic liver disease revealed by RNA sequencing.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:113422. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113422. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33007391
-
Comparison of dietary control and atorvastatin on high fat diet induced hepatic steatosis and hyperlipidemia in rats.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Jan 26;10:23. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-23. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 21269482 Free PMC article.
-
1,2,3,4,6 penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose ameliorates high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and maintains the expression of genes involved in lipid homeostasis in mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Sep;129:110348. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110348. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32554245
-
The immunoregulatory effects of scoparone on immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 31;16:1518886. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1518886. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39958341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Scoparone suppresses proliferation and cell cycle of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inhibiting AKT/GSK-3β/cyclin D1 signaling pathway.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 30;14(3):1638-1650. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1771. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40224969 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

