Whole-exome sequencing of a multicenter cohort identifies genetic changes associated with clinical phenotypes in pediatric nephrotic syndrome
- PMID: 36157477
- PMCID: PMC9485284
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.03.023
Whole-exome sequencing of a multicenter cohort identifies genetic changes associated with clinical phenotypes in pediatric nephrotic syndrome
Abstract
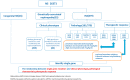
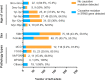
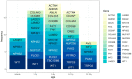
Understanding the association between the genetic and clinical phenotypes in children with nephrotic syndrome (NS) of different etiologies is critical for early clinical guidance. We employed whole-exome sequencing (WES) to detect monogenic causes of NS in a multicenter cohort of 637 patients. In this study, a genetic cause was identified in 30.0% of the idiopathic steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) patients. Other than congenital nephrotic syndrome (CNS), there were no significant differences in the incidence of monogenic diseases based on the age at manifestation. Causative mutations were detected in 39.5% of patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) and 9.2% of those with minimal change disease (MCD). In terms of the patterns in patients with different types of steroid resistance, a single gene mutation was identified in 34.8% of patients with primary resistance, 2.9% with secondary resistance, and 71.4% of children with multidrug resistance. Among the various intensified immunosuppressive therapies, tacrolimus (TAC) showed the highest response rate, with 49.7% of idiopathic SRNS patients achieving complete remission. Idiopathic SRNS patients with monogenic disease showed a similar multidrug resistance pattern, and only 31.4% of patients with monogenic disease achieved a partial remission on TAC. During an average 4.1-year follow-up, 21.4% of idiopathic SRNS patients with monogenic disease progressed to end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Collectively, this study provides evidence that genetic testing is necessary for presumed steroid-resistant and idiopathic SRNS patients, especially those with primary and/or multidrug resistance.
Keywords: Clinical phenotypes; Genetic phenotypes; Multicenter cohort; Nephrotic syndrome; Pediatric; Whole-exome sequencing.
© 2022 Chongqing Medical University. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Noone D.G., Iijima K., Parekh R. Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children. Lancet. 2018;392(10141):61–74. - PubMed
-
- Cattran D.C., Feehally J., Cook H.T., et al. Kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO) glomerulonephritis work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2012;2(2):139–274.
-
- Dufek S., Ylinen E., Trautmann A., et al. Infants with congenital nephrotic syndrome have comparable outcomes to infants with other renal diseases. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019;34(4):649–655. - PubMed
-
- Lombel R.M., Gipson D.S., Hodson E.M. Kidney Disease: improving Global Outcomes. Treatment of steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome: new guidelines from KDIGO. Pediatr Nephrol. 2013;28(3):415–426. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

