Stem cell therapy for insulin-dependent diabetes: Are we still on the road?
- PMID: 36157527
- PMCID: PMC9350623
- DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.503
Stem cell therapy for insulin-dependent diabetes: Are we still on the road?
Abstract
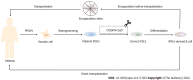
In insulin-dependent diabetes, the islet β cells do not produce enough insulin and the patients must receive exogenous insulin to control blood sugar. However, there are still many deficiencies in exogenous insulin supplementation. Therefore, the replacement of destroyed functional β cells with insulin-secreting cells derived from functional stem cells is a good idea as a new therapeutic idea. This review introduces the development schedule of mouse and human embryonic islets. The differences between mouse and human pancreas embryo development were also listed. Accordingly to the different sources of stem cells, the important research achievements on the differentiation of insulin-secreting β cells of stem cells and the current research status of stem cell therapy for diabetes were reviewed. Stem cell replacement therapy is a promising treatment for diabetes, caused by defective insulin secretion, but there are still many problems to be solved, such as the biosafety and reliability of treatment, the emergence of tumors during treatment, untargeted differentiation and autoimmunity, etc. Therefore, further understanding of stem cell therapy for insulin is needed.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Differentiation; Stem cell therapy; Transplantation; β cell.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Magliano DJ, Harding JL, Shaw JE. Glycemic control and excess mortality in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:880. - PubMed
-
- Khunti K, Davies M, Majeed A, Thorsted BL, Wolden ML, Paul SK. Hypoglycemia and risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in insulin-treated people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:316–322. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

