Coxsackievirus B infections are common in Cystic Fibrosis and experimental evidence supports protection by vaccination
- PMID: 36157581
- PMCID: PMC9490033
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105070
Coxsackievirus B infections are common in Cystic Fibrosis and experimental evidence supports protection by vaccination
Abstract
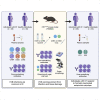
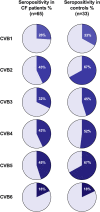
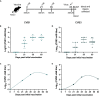
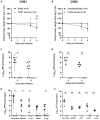
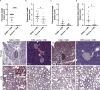
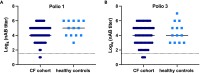
Viral respiratory tract infections exacerbate airway disease and facilitate life-threatening bacterial colonization in cystic fibrosis (CF). Annual influenza vaccination is recommended and vaccines against other common respiratory viruses may further reduce pulmonary morbidity risk. Enteroviruses have been found in nasopharyngeal samples from CF patients experiencing pulmonary exacerbations. Using serology tests, we found that infections by a group of enteroviruses, Coxsackievirus Bs (CVBs), are prevalent in CF. We next showed that a CVB vaccine, currently undergoing clinical development, prevents infection and CVB-instigated lung damage in a murine model of CF. Finally, we demonstrate that individuals with CF have normal vaccine responses to a similar, commonly used enterovirus vaccine (inactivated poliovirus vaccine). Our study demonstrates that CVB infections are common in CF and provides experimental evidence indicating that CVB vaccines could be efficacious in the CF population. The role of CVB infections in contributing to pulmonary exacerbations in CF should be further studied.
Keywords: Virology.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
H.H. owns stocks in, and is the chairman of, the board of Vactech Ltd that develops vaccines against picornaviruses. H.H. and M.F.T. serve on the scientific advisory board of Provention Bio Inc. that develops vaccines against Coxsackie B viruses in collaboration with Vactech Ltd. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Browning M.J., Lim M.T.C., Kenia P., Whittle M., Doffinger R., Barcenas-Morales G., Kumararatne D., Viskaduraki M., O'Callaghan C., Gaillard E.A. Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine responses are impaired in a subgroup of children with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2014;13:632–638. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2014.02.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dijkema J.S., van Ewijk B.E., Wilbrink B., Wolfs T.F.W., Kimpen J.L.L., van der Ent C.K. Frequency and duration of Rhinovirus infections in children with cystic fibrosis and healthy controls: a longitudinal cohort study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016;35:379–383. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000001014. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

