Tamsulosin-induced life-threatening hypotension in a patient with spinal cord injury: A case report
- PMID: 36157672
- PMCID: PMC9477057
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i25.9142
Tamsulosin-induced life-threatening hypotension in a patient with spinal cord injury: A case report
Abstract
Background: Tamsulosin, a selective α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist, is commonly used for treating neurogenic bladder in patients with spinal cord injury (SCI). No severe adverse events have been described with such tamsulosin use. To our knowledge, we report the first case of severe life-threatening hypotension as an adverse effect of tamsulosin in a person with SCI. Therefore, we report this case to inform that this severe adverse effect of tamsulosin can occur when treating patients with SCI.
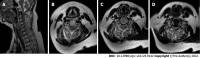
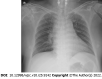
Case summary: A 59-year-old woman was diagnosed with cervical spinal cord myelopathy and was classified as American Spinal Injury Association Impairment Scale D, neurological level of injury C3. Because she suffered from voiding difficulty due to neurogenic bladder, we prescribed tamsulosin. Her vital signs remained stable, but occasional hypotensive symptoms followed defecation. We reduced the dose of tamsulosin, but after administering tamsulosin for 9 d, she experienced life-threatening hypotension with no evidence of hypovolemic shock, neurogenic shock, cardiogenic shock, or septic shock. A hypotensive condition induced by tamsulosin was the suspected cause, and her symptoms could be associated with adverse effects of tamsulosin. As symptoms resolved after stopping tamsulosin, and no other reason was found, we concluded that tamsulosin was the cause of her symptoms.
Conclusion: Caution for severe hypotension is needed when administering tamsulosin for neurogenic bladder in a patient with SCI.
Keywords: Case report; Hypotension; Neurogenic bladder; Spinal cord injury; Tamsulosin; Vasovagal symptoms.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Afferent Pathway-Mediated Effect of α1 Adrenergic Antagonist, Tamsulosin, on the Neurogenic Bladder After Spinal Cord Injury.Int Neurourol J. 2017 Sep;21(3):178-188. doi: 10.5213/inj.1734984.492. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Int Neurourol J. 2017. PMID: 28954467 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of bladder function by early tamsulosin treatment in a spinal cord injury rat model.Ann Rehabil Med. 2014 Aug;38(4):433-42. doi: 10.5535/arm.2014.38.4.433. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Ann Rehabil Med. 2014. PMID: 25229021 Free PMC article.
-
Transient alteration of consciousness in spinal cord injury secondary to Baclofen use: a case report.Spinal Cord Ser Cases. 2022 May 21;8(1):56. doi: 10.1038/s41394-022-00511-z. Spinal Cord Ser Cases. 2022. PMID: 35597797 Free PMC article.
-
Propantheline bromide in the management of hyperhidrosis associated with spinal cord injury.Ann Pharmacother. 1995 May;29(5):489-92. doi: 10.1177/106002809502900507. Ann Pharmacother. 1995. PMID: 7655132 Review.
-
Vascular dysfunctions following spinal cord injury.J Med Life. 2010 Jul-Sep;3(3):275-85. J Med Life. 2010. PMID: 20945818 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Orthostatic Hypotension in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Patients and Its Association With Alpha-1 Antagonist Use: A Comprehensive Literature Review.Cureus. 2023 Aug 25;15(8):e44097. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44097. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37750139 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chapple C, Andersson KE. Tamsulosin: an overview. World J Urol. 2002;19:397–404. - PubMed
-
- Abrams P, Amarenco G, Bakke A, Buczyński A, Castro-Diaz D, Harrison S, Kramer G, Marsik R, Prajsner A, Stöhrer M, Van Kerrebroeck P, Wyndaele JJ European Tamsulosin Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Study Group. Tamsulosin: efficacy and safety in patients with neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction due to suprasacral spinal cord injury. J Urol. 2003;170:1242–1251. - PubMed
-
- Meyer LE, Brown JN. Tamsulosin for voiding dysfunction in women. Int Urol Nephrol. 2012;44:1649–1656. - PubMed
-
- Zhang HL, Huang ZG, Qiu Y, Cheng X, Zou XQ, Liu TT. Tamsulosin for treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Impot Res. 2017;29:148–156. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

