Cisplatin for cancer therapy and overcoming chemoresistance
- PMID: 36158077
- PMCID: PMC9489975
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10608
Cisplatin for cancer therapy and overcoming chemoresistance
Abstract
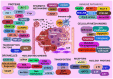
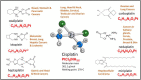
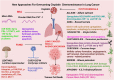
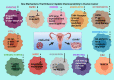
Cisplatin spearheads the anticancer chemotherapeutics in present-day use although acute toxicity is its primary impediment factor. Among a plethora of experimental medications, a drug as effective or surpassing the benefits of cisplatin has not been discovered yet. Although Oxaliplatin is considered more superior to cisplatin, the former has been better for colorectal cancer while cisplatin is widely used for treating gynaecological cancers. Carcinoma imposes a heavy toll on mortality rates worldwide despite the novel treatment strategies and detection methods that have been introduced; nanomedicine combined with precision medicine, immunotherapy, volume-regulated anion channels, and fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography. Millions of deaths occur annually from metastatic cancers which escape early detection and the concomitant diseases caused by highly toxic chemotherapy that causes organ damage. It continues due to insufficient knowledge of the debilitative mechanisms induced by cancer biology. To overcome chemoresistance and to attenuate the adverse effects of cisplatin therapy, both in vitro and in vivo models of cisplatin-treated cancers and a few multi-centred, multi-phasic, randomized clinical trials in pursuant with recent novel strategies have been tested. They include plant-based phytochemical compounds, de novo drug delivery systems, biochemical/immune pathways, 2D and 3D cell culture models using small molecule inhibitors and genetic/epigenetic mechanisms, that have contributed to further the understanding of cisplatin's role in modulating the tumour microenvironment. Cisplatin was beneficial in cancer therapy for modulating the putative cellular mechanisms; apoptosis, autophagy, cell cycle arrest and gene therapy of micro RNAs. Specific importance of drug influx, efflux, systemic circulatory toxicity, half-maximal inhibition, and the augmentation of host immunometabolism have been identified. This review offers a discourse on the recent anti-neoplastic treatment strategies to enhance cisplatin efficacy and to overcome chemoresistance, given its superiority among other tolerable chemotherapies.
Keywords: Cancer; Cancer biology; Cancer epidemiology; Cancer therapy; Chemoresistance; Chemotherapy; Cisplatin; Immunology; New advances in cisplatin therapy.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sung H., et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Sayyed A.A., et al. MiR-155 inhibitor-laden exosomes reverse resistance to cisplatin in a 3D tumor spheroid and xenograft model of oral cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2021;18(8):3010–3025. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

