Hepatitis B and circadian rhythm of the liver
- PMID: 36158265
- PMCID: PMC9346465
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i27.3282
Hepatitis B and circadian rhythm of the liver
Abstract
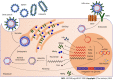
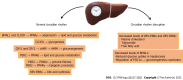
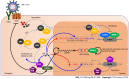
The circadian rhythm in humans is determined by the central clock located in the hypothalamus's suprachiasmatic nucleus, and it synchronizes the peripheral clocks in other tissues. Circadian clock genes and clock-controlled genes exist in almost all cell types. They have an essential role in many physiological processes, including lipid metabolism in the liver, regulation of the immune system, and the severity of infections. In addition, circadian rhythm genes can stimulate the immune response of host cells to virus infection. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is the leading cause of liver disease and liver cancer globally. HBV infection depends on the host cell, and hepatocyte circadian rhythm genes are associated with HBV replication, survival, and spread. The core circadian rhythm proteins, REV-ERB and brain and muscle ARNTL-like protein 1, have a crucial role in HBV replication in hepatocytes. In addition to influencing the virus's life cycle, the circadian rhythm also affects the pharmacokinetics and efficacy of antiviral vaccines. Therefore, it is vital to apply antiviral therapy at the appropriate time of day to reduce toxicity and improve the effectiveness of antiviral treatment. For these reasons, understanding the role of the circadian rhythm in the regulation of HBV infection and host responses to the virus provides us with a new perspective of the interplay of the circadian rhythm and anti-HBV therapy. Therefore, this review emphasizes the importance of the circadian rhythm in HBV infection and the optimization of antiviral treatment based on the circadian rhythm-dependent immune response.
Keywords: Circadian rhythm; Clock genes; Hepatitis B virus; Immune system; Liver.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: There are no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Circadian Clock and Viral Infections.J Biol Rhythms. 2021 Feb;36(1):9-22. doi: 10.1177/0748730420967768. Epub 2020 Nov 9. J Biol Rhythms. 2021. PMID: 33161818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hepatic circadian clock regulates the choline kinase α gene through the BMAL1-REV-ERBα axis.Chronobiol Int. 2015;32(6):774-84. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2015.1046601. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Chronobiol Int. 2015. PMID: 26125130
-
Circadian clock dysfunction of epithelial cells in pulmonary diseases.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021 Dec;141:106110. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2021.106110. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34699979 Review.
-
Effect of H₂S on the circadian rhythm of mouse hepatocytes.Lipids Health Dis. 2012 Feb 8;11:23. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-23. Lipids Health Dis. 2012. PMID: 22316301 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel circadian clock modulator controlling BMAL1 expression through a ROR/REV-ERB-response element-dependent mechanism.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Jan 15;469(3):580-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.12.030. Epub 2015 Dec 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 26692477
Cited by
-
Circadian control of ConA-induced acute liver injury and inflammatory response via Bmal1 regulation of Junb.JHEP Rep. 2023 Jul 22;5(11):100856. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100856. eCollection 2023 Nov. JHEP Rep. 2023. PMID: 37791375 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of circadian clock to the biological processes.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jun 6;11:1387576. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1387576. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38903177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetes mellitus and glymphatic dysfunction: Roles for oxidative stress, mitochondria, circadian rhythm, artificial intelligence, and imaging.World J Diabetes. 2025 Jan 15;16(1):98948. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i1.98948. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 39817214 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

