Capecitabine-Associated Coronary Vasospasm and Cardiac Arrest
- PMID: 36158449
- PMCID: PMC9482813
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.28184
Capecitabine-Associated Coronary Vasospasm and Cardiac Arrest
Abstract
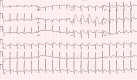
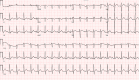
Capecitabine is a prodrug of fluorouracil that specifically targets cancer cells, commonly used as monotherapy for metastatic breast and colorectal cancer. Its side effects include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, anorexia, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, anemia, and hyperbilirubinemia. Rarely, this chemotherapy agent has been associated with cardiotoxicity, including cardiac arrest, likely secondary to coronary vasospasm. This case report serves to highlight the unfortunate case of a 32-year-old female who suffered a ventricular fibrillation cardiac arrest three days after initiating capecitabine therapy.
Keywords: breast cancer; capecitabine; cardiac arrest; coronary vasospasm; ventricular fibrillation.
Copyright © 2022, Muco et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Multicenter phase II study of capecitabine in paclitaxel-refractory metastatic breast cancer. Blum JL, Jones SE, Buzdar AU, et al. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:485–493. - PubMed
-
- Capecitabine-induced ventricular fibrillation [Article in Dutch] Van Capelle AV, de Valk J, Schakenraad D, et al. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28074721/ Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2017;160:0. - PubMed
-
- Capecitabine-induced ventricular fibrillation arrest: possible Kounis syndrome. Kido K, Adams VR, Morehead RS, Flannery AH. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016;22:335–340. - PubMed
-
- Drugs that may cause or exacerbate heart failure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Page RL 2nd, O'Bryant CL, Cheng D, et al. Circulation. 2016;6:261. - PubMed
-
- Fluoropyrimidine-associated cardiotoxicity. Kanduri J, More LA, Godishala A, Asnani A. Cardiol Clin. 2019;37:399–405. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources