Overview of methods for characterization and visualization of a protein-protein interaction network in a multi-omics integration context
- PMID: 36158572
- PMCID: PMC9494275
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.962799
Overview of methods for characterization and visualization of a protein-protein interaction network in a multi-omics integration context
Abstract
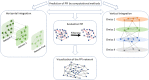
At the heart of the cellular machinery through the regulation of cellular functions, protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have a significant role. PPIs can be analyzed with network approaches. Construction of a PPI network requires prediction of the interactions. All PPIs form a network. Different biases such as lack of data, recurrence of information, and false interactions make the network unstable. Integrated strategies allow solving these different challenges. These approaches have shown encouraging results for the understanding of molecular mechanisms, drug action mechanisms, and identification of target genes. In order to give more importance to an interaction, it is evaluated by different confidence scores. These scores allow the filtration of the network and thus facilitate the representation of the network, essential steps to the identification and understanding of molecular mechanisms. In this review, we will discuss the main computational methods for predicting PPI, including ones confirming an interaction as well as the integration of PPIs into a network, and we will discuss visualization of these complex data.
Keywords: biological network; computational prediction; graphic view; integrated strategies; interactome; protein-protein interaction.
Copyright © 2022 Robin, Bodein, Scott-Boyer, Leclercq, Périn and Droit.
Conflict of interest statement
Author OP is employed by company L'Oréal. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Affeldt S., Sokolovska N., Prifti E., Zucker J. D. (2016). Spectral consensus strategy for accurate reconstruction of large biological networks. BMC Bioinforma. 17 (16), 493. 10.1186/s12859-016-1308-y PubMed Abstract | 10.1186/s12859-016-1308-y | Google Scholar - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agapito G., Guzzi P. H., Cannataro M. (2013). Visualization of protein interaction networks: Problems and solutions. BMC Bioinforma. 14 (1), S1. 10.1186/1471-2105-14-S1-S1 PubMed Abstract | 10.1186/1471-2105-14-S1-S1 | Google Scholar - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aghakhani S., Qabaja A., Alhajj R. (2018). Integration of k-means clustering algorithm with network analysis for drug-target interactions network prediction. Int. J. Data Min. Bioinform. 20, 185. 10.1504/IJDMB.2018.10016075 10.1504/IJDMB.2018.10016075 | Google Scholar - DOI - DOI
-
- Ahmed I., Witbooi P., Christoffels A. (2018). Prediction of human-Bacillus anthracis protein-protein interactions using multi-layer neural network. Bioinforma. Oxf. Engl. 34 (24), 4159–4164. 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty504 PubMed Abstract | 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty504 | Google Scholar - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed M. (2020). Modified naive Bayes classifier for classification of protein- protein interaction sites. J. Biosci. Agric. Res. 26, 2177–2184. 10.18801/jbar.260220.266 10.18801/jbar.260220.266 | Google Scholar - DOI - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

