Multimodal resting-state connectivity predicts affective neurofeedback performance
- PMID: 36158618
- PMCID: PMC9493361
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.977776
Multimodal resting-state connectivity predicts affective neurofeedback performance
Abstract
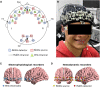
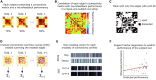
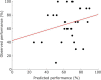
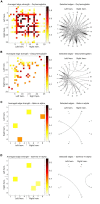
Neurofeedback has been suggested as a potential complementary therapy to different psychiatric disorders. Of interest for this approach is the prediction of individual performance and outcomes. In this study, we applied functional connectivity-based modeling using electroencephalography (EEG) and functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) modalities to (i) investigate whether resting-state connectivity predicts performance during an affective neurofeedback task and (ii) evaluate the extent to which predictive connectivity profiles are correlated across EEG and fNIRS techniques. The fNIRS oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin concentrations and the EEG beta and gamma bands modulated by the alpha frequency band (beta-m-alpha and gamma-m-alpha, respectively) recorded over the frontal cortex of healthy subjects were used to estimate functional connectivity from each neuroimaging modality. For each connectivity matrix, relevant edges were selected in a leave-one-subject-out procedure, summed into "connectivity summary scores" (CSS), and submitted as inputs to a support vector regressor (SVR). Then, the performance of the left-out-subject was predicted using the trained SVR model. Linear relationships between the CSS across both modalities were evaluated using Pearson's correlation. The predictive model showed a mean absolute error smaller than 20%, and the fNIRS oxyhemoglobin CSS was significantly correlated with the EEG gamma-m-alpha CSS (r = -0.456, p = 0.030). These results support that pre-task electrophysiological and hemodynamic resting-state connectivity are potential predictors of neurofeedback performance and are meaningfully coupled. This investigation motivates the use of joint EEG-fNIRS connectivity as outcome predictors, as well as a tool for functional connectivity coupling investigation.
Keywords: brain connectivity; electroencephalography; functional near-infrared spectroscopy; neurofeedback; resting-state.
Copyright © 2022 Trambaiolli, Cassani, Biazoli, Cravo, Sato and Falk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Akhtar M. T., Mitsuhashi W., James C. J. (2012). Employing spatially constrained ica and wavelet denoising, for automatic removal of artifacts from multichannel EEG data. Signal Proc. 92 401–416.
-
- Babiloni C., Vecchio F., Altavilla R., Tibuzzi F., Lizio R., Altamura C., et al. (2014). Hypercapnia affects the functional coupling of resting state electroencephalographic rhythms and cerebral haemodynamics in healthy elderly subjects and in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Clin. Neurophysiol. 125 685–693. 10.1016/j.clinph.2013.10.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bagherzadeh Y., Baldauf D., Pantazis D., Desimone R. (2020). Alpha synchrony and the neurofeedback control of spatial attention. Neuron 105 577–587.e5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

