Plastic surgery and adjuvant chemoradiotherapy in the management of advanced external auditory canal cancer
- PMID: 36158980
- PMCID: PMC9458265
- DOI: 10.3332/ecancer.2022.1432
Plastic surgery and adjuvant chemoradiotherapy in the management of advanced external auditory canal cancer
Abstract
Background: Carcinoma of the external auditory canal is a rare malignancy that originates in the external auditory canal and has a tendency to spread to adjacent structures such as the periorbital soft tissues, parotid gland, temporomandibular joint and mastoid. It is difficult to determine the primary tumour from the external ear canal or from adjacent structures. In addition, the lack of a unified classification system, along with the rarity of the disease, is a major obstacle in providing specific treatment guidelines for this disease.
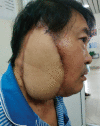
Case presentation: In this report, we describe a clinical case of a 59-year-old male patient who was admitted to the hospital because of ear pain and discharge from the outer ear canal with swelling in the right temporal region. The initial diagnosis is highly suggestive of an advanced external auditory canal malignancy with involvement of the parotid gland. The patient underwent surgery to remove the entire tumour, neck lymph nodes, followed by plastic surgery. The patient then received adjuvant chemoradiotherapy. There was no recurrence of cancer for 28 months, to date, after completing treatment.
Conclusions: Extensive tumour resection combined with reconstruction and adjuvant chemoradiotherapy is a treatment strategy with good outcomes for patients with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the external ear canal.
Keywords: advanced stages; chemoradiotherapy; external auditory canal; squamous cell carcinoma.
© the authors; licensee ecancermedicalscience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Zhen S, Fu T, Qi J. Diagnosis and treatment of carcinoma in external auditory canal. J Otol. 2014;9(3):146–150. doi: 10.1016/j.joto.2014.12.004. - DOI
-
- Żurek M, Rzepakowska A, Niemczyk K. Difficulties in clinical staging of external ear canal carcinoma – a case report. Polski Przegląd Otorynolaryngologiczny. 2018;7:30–35. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0011.6697. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
