An Updated Algorithm Integrated With Patient Data for the Differentiation of Atypical Nevi From Early Melanomas: the idScore 2021
- PMID: 36159145
- PMCID: PMC9464562
- DOI: 10.5826/dpc.1203a134
An Updated Algorithm Integrated With Patient Data for the Differentiation of Atypical Nevi From Early Melanomas: the idScore 2021
Abstract
Introduction: It is well known that multiple patient-related risk factors contribute to the development of cutaneous melanoma, including demographic, phenotypic and anamnestic factors.
Objectives: We aimed to investigate which MM risk factors were relevant to be incorporated in a risk scoring-classifier based clinico-dermoscopic algorithm.
Methods: This retrospective study was performed on a monocentric dataset of 374 atypical melanocytic skin lesions sharing equivocal dermoscopic features, excised in the suspicion of malignancy. Dermoscopic standardized images of 258 atypical nevi (aN) and 116 early melanomas (eMM) were collected along with objective lesional data (i.e., maximum diameter, specific body site and body area) and 7 dermoscopic data. All cases were combined with a series of 10 MM risk factors, including demographic (2), phenotypic (5) and anamnestic (3) ones.
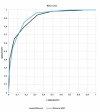
Results: The proposed iDScore 2021 algorithm is composed by 9 variables (age, skin phototype I/II, personal/familiar history of MM, maximum diameter, location on the lower extremities (thighs/legs/ankles/back of the feet) and 4 dermoscopic features (irregular dots and globules, irregular streaks, blue gray peppering, blue white veil). The algorithm assigned to each lesion a score from 0 to 18, reached an area under the ROC curve of 92% and, with a score threshold ≥ 6, a sensitivity (SE) of 98.2% and a specificity (SP) of 50.4%, surpassing the experts in SE (+13%) and SP (+9%).
Conclusions: An integrated checklist combining multiple anamnestic data with selected relevant dermoscopic features can be useful in the differential diagnosis and management of eMM and aN exhibiting with equivocal features.
Keywords: atypical nevi; dermoscopy; melanoma; risk factors.
©2022 Tognetti et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Figures










Similar articles
-
An integrated clinical-dermoscopic risk scoring system for the differentiation between early melanoma and atypical nevi: the iDScore.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Dec;32(12):2162-2170. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15106. Epub 2018 Jun 28. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018. PMID: 29888421
-
Impact of clinical and personal data in the dermoscopic differentiation between early melanoma and atypical nevi.Dermatol Pract Concept. 2018 Oct 31;8(4):324-327. doi: 10.5826/dpc.0804a16. eCollection 2018 Oct. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2018. PMID: 30479866 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Histopathologic Characteristics of Melanocytic Lesions on the Volar Skin Without Typical Dermoscopic Patterns.JAMA Dermatol. 2019 May 1;155(5):578-584. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.5926. JAMA Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30865233 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy of Dermoscopic Structures and Patterns Used in Melanoma Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Dermatol. 2021 Sep 1;157(9):1078-1088. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2845. JAMA Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34347005 Free PMC article.
-
Role of In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy in the Analysis of Melanocytic Lesions.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018 Apr;26(1):64-67. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018. PMID: 29782304 Review.
Cited by
-
A European Multicentric Investigation of Atypical Melanocytic Skin Lesions of Palms and Soles: The iDScore-PalmoPlantar Database.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 20;14(5):460. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14050460. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38472933 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of AI Models for Atypical Pigmented Facial Lesion Diagnosis.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Oct 17;11(10):1036. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11101036. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451411 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Automatic Melanoma Diagnosis Using Deep Learning-Based Segmentation of Irregular Networks.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 16;15(4):1259. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041259. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831599 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
