Machine learning techniques for CT imaging diagnosis of novel coronavirus pneumonia: a review
- PMID: 36159188
- PMCID: PMC9483435
- DOI: 10.1007/s00521-022-07709-0
Machine learning techniques for CT imaging diagnosis of novel coronavirus pneumonia: a review
Abstract
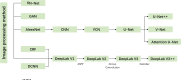
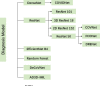
Since 2020, novel coronavirus pneumonia has been spreading rapidly around the world, bringing tremendous pressure on medical diagnosis and treatment for hospitals. Medical imaging methods, such as computed tomography (CT), play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating COVID-19. A large number of CT images (with large volume) are produced during the CT-based medical diagnosis. In such a situation, the diagnostic judgement by human eyes on the thousands of CT images is inefficient and time-consuming. Recently, in order to improve diagnostic efficiency, the machine learning technology is being widely used in computer-aided diagnosis and treatment systems (i.e., CT Imaging) to help doctors perform accurate analysis and provide them with effective diagnostic decision support. In this paper, we comprehensively review these frequently used machine learning methods applied in the CT Imaging Diagnosis for the COVID-19, discuss the machine learning-based applications from the various kinds of aspects including the image acquisition and pre-processing, image segmentation, quantitative analysis and diagnosis, and disease follow-up and prognosis. Moreover, we also discuss the limitations of the up-to-date machine learning technology in the context of CT imaging computer-aided diagnosis.
Keywords: Aided diagnosis; COVID-19; CT imaging; Machine learning.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag London Ltd., part of Springer Nature 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A new approach for computer-aided detection of coronavirus (COVID-19) from CT and X-ray images using machine learning methods.Appl Soft Comput. 2021 Jul;105:107323. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107323. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Appl Soft Comput. 2021. PMID: 33746657 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiating novel coronavirus pneumonia from general pneumonia based on machine learning.Biomed Eng Online. 2020 Aug 19;19(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12938-020-00809-9. Biomed Eng Online. 2020. PMID: 32814568 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Imaging Data Acquisition, Segmentation, and Diagnosis for COVID-19.IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2021;14:4-15. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2020.2987975. Epub 2021 Jan 22. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2021. PMID: 32305937 Review.
-
Lung Lesion Localization of COVID-19 From Chest CT Image: A Novel Weakly Supervised Learning Method.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2021 Jun;25(6):1864-1872. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3067465. Epub 2021 Jun 3. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2021. PMID: 33739926 Free PMC article.
-
Application of machine learning in CT images and X-rays of COVID-19 pneumonia.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Sep 10;100(36):e26855. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026855. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34516488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research on the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Public Health Management: Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Improve COVID-19 CT Image Diagnosis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 9;20(2):1158. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20021158. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36673913 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Evolution: Implications for Diagnosis, Treatment, Vaccine Effectiveness and Development.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Dec 28;13(1):17. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13010017. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39852796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid detection of non-normal teeth on dental X-ray images using improved Mask R-CNN with attention mechanism.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024 Apr;19(4):779-790. doi: 10.1007/s11548-023-03047-1. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024. PMID: 38170416
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources