Therapeutic Application of Lithium in Bipolar Disorders: A Brief Review
- PMID: 36159362
- PMCID: PMC9484534
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.29332
Therapeutic Application of Lithium in Bipolar Disorders: A Brief Review
Abstract
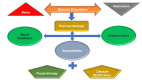
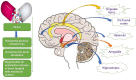
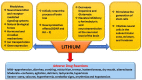
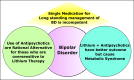
Bipolar affective disorder includes Bipolar Disease (BD) and Bipolar Spectrum Disorder (BSD). The prevalence of BSD, BD-I, BD-II, and subthreshold BD globally is estimated to be about 3.1%, 1.5%,0.03%, and 1.6%, respectively. BD is a multidimensional disease that exhibits a range of moods of mania, hypomania, and depression. The disease is chronic, complex, and fatal, with a high possibility of reappearance, infirmity, social incompetence, and felo-de-se. Managing emotional disruption, negative neuropsychology, physiology, and immunology is a challenge. This review focuses on therapeutic benefits, adverse drug reactions, and pharmacological intervention for BD and BSD, in particular lithium. Long-term management of BD with a single medication is ineffective and therefore, not recommended. It is advised to use multiple agents for treatment instead. Medications include mood stabilizers (lithium and anticonvulsants), atypical antipsychotics, and antidepressants. Along with medication provision, psychotherapy is of great significance for BD patients. The review was conducted on recent available scientific literature through the electronic database like Embase, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, and PubMed using keywords like 'Bipolar Disease,' 'Bipolar Disease Therapeutics,' 'Bipolar Disease and Psychotherapy' to highlight the possible effective means of management of this disease of mood instability.
Keywords: bipolar disorders; bipolar spectrum disorder; fda-approved medications; history of bipolar disorders; intervention; lithium; narrative review; nhs approved medications; pharmacological treatment; treatment modalities.
Copyright © 2022, Kamal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Pharmacotherapeutic interventions for bipolar disorder type II: addressing multiple symptoms and approaches with a particular emphasis on strategies in lower and middle-income countries. Godman B, Grobler C, Van-De-Lisle M, et al. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2019;20:2237–2255. - PubMed
-
- Prevalence and correlates of bipolar spectrum disorders in Singapore: Results from the 2016 Singapore Mental Health Study (SMHS 2016) Teh WL, Abdin E, Vaingankar J, et al. J Affect Disord. 2020;274:339–346. - PubMed
-
- Intervention trials for adults with bipolar disorder in low-income and lower-middle-income countries: a systematic review. Arnbjerg CJ, Rurangwa NU, Musoni-Rwililiza E, Gishoma D, Carlsson J, Kallestrup P. J Affect Disord. 2022;311:256–266. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
