Vitamin D supplementation positively affects anthropometric indices: Evidence obtained from an umbrella meta-analysis
- PMID: 36159504
- PMCID: PMC9490226
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.980749
Vitamin D supplementation positively affects anthropometric indices: Evidence obtained from an umbrella meta-analysis
Abstract
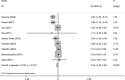
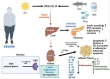
Despite the growing evidence from meta-analyses on vitamin D's anti-obesity properties, their results are controversial. The current umbrella review was performed to assess the available evidence and provide a conclusive explanation in this regard. The international databases PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science and Google Scholar were systematically searched till March, 2022. A random-effects model was used to run the meta-analysis. All meta-analyses that examined the effect of vitamin D supplementation on BW, BMI, WC, and fat mass were included. Findings of 14 meta-analyses revealed that vitamin D supplementation reduced body mass index (BMI) (ES: -0.11 kg/m2; 95% CI: -0.18, -0.05, p?0.001; I 2 = 61.0%, p < 0.001), and waist circumference (WC) (ES = -0.79 cm; 95% CI: -1.20, -0.37; p < 0.001; I 2 = 46.5%, p = 0.096) in comparison to control group. However, the effects of vitamin D on body weight (ES = -0.16 kg, 95% CI: -0.36, 0.04; p = 0.125; I 2 = 57.0%, p = 0.017), and fat mass (ES: 0.02, 95% CI: -0.20, 0.24, p = 0.868; I 2 = 0.0%, p = 0.531) were not considerable. Vitamin D supplementation significantly improved levels of obesity indices such as BMI, and WC.
Keywords: anthropometric indices; body mass index; obesity; umbrella meta-analysis; vitamin D.
Copyright © 2022 Musazadeh, Zarezadeh, Ghalichi, Kalajahi and Ghoreishi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anti-obesity properties of probiotics; a considerable medical nutrition intervention: Findings from an umbrella meta-analysis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 5;928:175069. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175069. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35659967 Review.
-
Effects of synbiotics supplementation on anthropometric and lipid profile parameters: Finding from an umbrella meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2023 Feb 23;10:1121541. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1121541. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36908920 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of curcumin supplementation on weight loss and anthropometric indices: an umbrella review and updated meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials.Am J Clin Nutr. 2023 May;117(5):1005-1016. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.03.006. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Am J Clin Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36898635
-
The Effect of the L-Carnitine Supplementation on Obesity Indices: An Umbrella Meta-Analysis.Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2025 Apr 28;95(2):40033. doi: 10.31083/IJVNR40033. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2025. PMID: 40298161
-
Effects of resveratrol on the anthropometric indices and inflammatory markers: an umbrella meta-analysis.Eur J Nutr. 2024 Jun;63(4):1023-1040. doi: 10.1007/s00394-024-03335-9. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Eur J Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38374352
Cited by
-
Vitamin D Enhancement of Adipose Biology: Implications on Obesity-Associated Cardiometabolic Diseases.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 6;17(3):586. doi: 10.3390/nu17030586. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39940444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Cornus mas L. on Anthropometric Indices and Body Composition.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jul 15;13(7):e70404. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70404. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40666824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D deficiency prevention policies in Iran: a retrospective policy analysis.Front Nutr. 2023 Aug 23;10:1249402. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1249402. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37680901 Free PMC article.
-
Priority nutrients to address malnutrition and diet-related diseases in Australia and New Zealand.Front Nutr. 2024 Mar 13;11:1370550. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1370550. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38544756 Free PMC article.
-
The role of vitamin D in sleep regulation: mechanisms, clinical advances, and future directions.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 2;12:1595813. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1595813. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40529426 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- CDC. Overweight and Obesity. Atlanta, GA: CDC; (2018).
-
- WHO. Overweight and Obesity. Geneva: WHO; (2020).
-
- Thomas-Valdés S, Tostes MDGV, Anunciação PC, da Silva BP, Sant’Ana HMP. Association between vitamin deficiency and metabolic disorders related to obesity. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2017) 57:3332–43. - PubMed
-
- Aarts E, van Groningen L, Horst R, Telting D, van Sorge A, Janssen I, et al. Vitamin D absorption: consequences of gastric bypass surgery. Eur J Endocrinol. (2011) 164:827. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

