FBXW7 Reduces the Cancer Stem Cell-Like Properties of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Regulating the Ubiquitination and Degradation of ACTL6A
- PMID: 36159747
- PMCID: PMC9492413
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3242482
FBXW7 Reduces the Cancer Stem Cell-Like Properties of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Regulating the Ubiquitination and Degradation of ACTL6A
Abstract
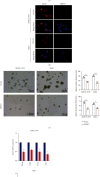
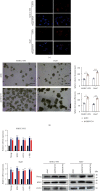
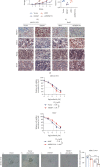
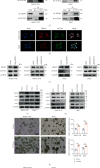
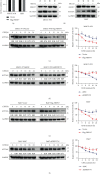
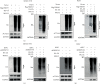
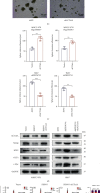
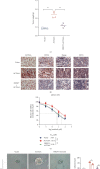
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) comprise a subset of tumor cells that can initiate tumorigenesis and promote tumor advance. A previous study showed that the expression of FBXW7 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) clinical samples was lower than that in the adjacent nontumor tissues and was negatively correlated with the invasion and migration of HCC cells. However, the biological characteristics and the underlying molecular mechanisms of FBXW7 in HCC stemness are yet to be elucidated. In present study, we found that FBXW7 participates in the self-renewal, tumorigenicity, sorafenib therapy, and stem cell-like properties of HCC cells in vivo and in vitro. The upregulation of FBXW7 inhibited the stemness and reduced the tumorigenicity and drug resistance of HCC cells. Mechanistically, proteins binding to FBXW7 were identified by coimmunoprecipitation and protein colocalization assays. We confirmed ACTL6A as a novel downstream target for FBXW7. The in vivo ubiquitination assay showed that FBXW7 repressed HCC malignancy by regulating the oncogenic activity of ACTL6A in a ubiquitin-dependent manner. Furthermore, we found that ACTL6A overexpression inversed the self-renewal abilities and tumorigenic abilities depressed by overexpressing FBXW7. The current findings suggested that FBXW7 reduces the stemness of HCC cells by targeting and degrading ACTL6A and provides a novel target for the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
Copyright © 2022 Xing Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fbxw7 is an independent prognostic marker and induces apoptosis and growth arrest by regulating YAP abundance in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2014 May 17;13:110. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-110. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24884509 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-25 Exerts an Oncogenic Function by Regulating the Ubiquitin Ligase Fbxw7 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Ann Surg Oncol. 2021 Nov;28(12):7973-7982. doi: 10.1245/s10434-021-09778-2. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33886022
-
FBXO9 Mediates the Cancer-Promoting Effects of ZNF143 by Degrading FBXW7 and Facilitates Drug Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 30;12:930220. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.930220. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847937 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Stem Cell Functions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies.Cells. 2020 May 26;9(6):1331. doi: 10.3390/cells9061331. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32466488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer Stem Cells: A Potential Breakthrough in HCC-Targeted Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 6;11:198. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00198. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32210805 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-182-5p promotes the proliferation and invasion of hilar cholangiocarcinoma cells by inhibiting FBXW7.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Oct 15;150(10):461. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05961-6. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39402299 Free PMC article.
-
Actin-Like Protein 6A as an Oncogene and Therapeutic Target in Cancer.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Jun 12;22(12):2906-2918. doi: 10.7150/ijms.113736. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40657395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fbxw7 suppresses carcinogenesis and stemness in triple-negative breast cancer through CHD4 degradation and Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibition.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 24;22(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04897-2. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38268032 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic ubiquitination networks in liver cancer: decoding E3 ligases and deubiquitinases as gatekeepers of therapeutic resistance.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 20;42(8):352. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02912-0. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40684404 Review.
-
Circ_0084615 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition-mediated tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma.Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2024 Jun 3;8(6):1107-1117. doi: 10.1002/ags3.12828. eCollection 2024 Nov. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2024. PMID: 39502735 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

