Breakthrough infections with the omicron and delta variants of SARS-CoV-2 result in similar re-activation of vaccine-induced immunity
- PMID: 36159859
- PMCID: PMC9493489
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.964525
Breakthrough infections with the omicron and delta variants of SARS-CoV-2 result in similar re-activation of vaccine-induced immunity
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Breakthrough infections with the omicron and delta variants of SARS-CoV-2 result in similar re-activation of vaccine-induced immunity.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 12;14:1249100. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1249100. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37503347 Free PMC article.
Abstract
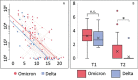
Background: Results showing that sera from double vaccinated individuals have minimal neutralizing activity against Omicron have been interpreted as indicating the need for a third vaccine dose for protection. However, there is little information about early immune responses to Omicron infection in double vaccinated individuals.
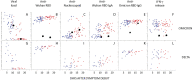
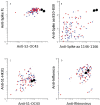
Methods: We measured inflammatory mediators, antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins, and spike peptide-induced release of interferon gamma in whole blood in 51 double-vaccinated individuals infected with Omicron, in 14 infected with Delta, and in 18 healthy controls. The median time points for the first and second samples were 7 and 14 days after symptom onset, respectively.
Findings: Infection with Omicron or Delta led to a rapid and similar increase in antibodies to the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of Omicron protein and spike peptide-induced interferon gamma in whole blood. Both the Omicron- and the Delta-infected patients had a mild and transient increase in inflammatory parameters.
Interpretation: The results suggest that two vaccine doses are sufficient to mount a rapid and potent immune response upon infection in healthy individuals of with the Omicron variant.
Funding: The study was funded by the Oslo University Hospital, and by grants from The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, Research Council of Norway (no 312780, 324272), South-Eastern Norway Regional Health Authority (no 2019067, 2021071, 10357, 2021047, 33612, 2021087, 2017092), EU Horizon 2020 grant no 848099, a philantropic donation from Vivaldi Invest A/S, and The European Virus Archive Global.
Keywords: Breakthrough infection; SARS-CoV-2; antibody; cellular immunity; human; vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 Søraas, Grødeland, Granerud, Ueland, Lind, Fevang, Murphy, Huse, Nygaard, Steffensen, al-Baldawi, Holberg-Petersen, Andresen, Ågnes, Ranheim, Schanke, Istre, Dahl, Chopra, Dudman, Kaarbø, Andersen, Vaage, Tran, Vaage, Michelsen, Müller, Aukrust, Halvorsen, Dahl, Holter and Lund-Johansen.
Conflict of interest statement
Author AS reports being an employee and shareholder at Age Labs outside of the submitted work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial and financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

