Calcium channels and transporters: Roles in response to biotic and abiotic stresses
- PMID: 36161014
- PMCID: PMC9493244
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.964059
Calcium channels and transporters: Roles in response to biotic and abiotic stresses
Abstract
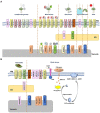
Calcium (Ca2+) serves as a ubiquitous second messenger by mediating various signaling pathways and responding to numerous environmental conditions in eukaryotes. Therefore, plant cells have developed complex mechanisms of Ca2+ communication across the membrane, receiving the message from their surroundings and transducing the information into cells and organelles. A wide range of biotic and abiotic stresses cause the increase in [Ca2+]cyt as a result of the Ca2+ influx permitted by membrane-localized Ca2+ permeable cation channels such as CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE-GATE CHANNELs (CNGCs), and voltage-dependent HYPERPOLARIZATION-ACTIVATED CALCIUM2+ PERMEABLE CHANNELs (HACCs), as well as GLUTAMATE RECEPTOR-LIKE RECEPTORs (GLRs) and TWO-PORE CHANNELs (TPCs). Recently, resistosomes formed by some NUCLEOTIDE-BINDING LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT RECEPTORs (NLRs) are also proposed as a new type of Ca2+ permeable cation channels. On the contrary, some Ca2+ transporting membrane proteins, mainly Ca2+-ATPase and Ca2+/H+ exchangers, are involved in Ca2+ efflux for removal of the excessive [Ca2+]cyt in order to maintain the Ca2+ homeostasis in cells. The Ca2+ efflux mechanisms mediate the wide ranges of cellular activities responding to external and internal stimuli. In this review, we will summarize and discuss the recent discoveries of various membrane proteins involved in Ca2+ influx and efflux which play an essential role in fine-tuning the processing of information for plant responses to abiotic and biotic stresses.
Keywords: Ca2+ efflux; Ca2+ influx; abiotic stress; biotic stress; calcium; channels; transporters.
Copyright © 2022 Park and Shin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
P-type calcium ATPases play important roles in biotic and abiotic stress signaling.Planta. 2024 Jun 26;260(2):37. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04462-7. Planta. 2024. PMID: 38922354 Review.
-
Mechanisms of cytosolic calcium elevation in plants: the role of ion channels, calcium extrusion systems and NADPH oxidase-mediated 'ROS-Ca2+ Hub'.Funct Plant Biol. 2018 Jan;45(2):9-27. doi: 10.1071/FP16420. Funct Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 32291018
-
Calcium efflux systems in stress signaling and adaptation in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2011 Dec 2;2:85. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2011.00085. eCollection 2011. Front Plant Sci. 2011. PMID: 22639615 Free PMC article.
-
A type of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel on Vicia faba guard cell plasma membrane outwardly permeates K+.Protoplasma. 2012 Jul;249(3):699-708. doi: 10.1007/s00709-011-0313-2. Epub 2011 Sep 3. Protoplasma. 2012. PMID: 21892599
-
Roles of Glutamate Receptor-Like Channels (GLRs) in Plant Growth and Response to Environmental Stimuli.Plants (Basel). 2022 Dec 9;11(24):3450. doi: 10.3390/plants11243450. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559561 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The physio-biochemical characterization reflected different calcium utilization efficiency between the sensitive and tolerant peanut accessions under calcium deficiency.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Aug 21;14:1250064. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1250064. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37670856 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive transcriptome analyses of Northern Wild Rice (Zizania palustris L.) and Bipolaris oryzae show convoluted communications during the early stages of fungal brown spot development.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Apr 26;15:1350281. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1350281. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38736448 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigating toxic metals contamination in foods: Bridging knowledge gaps for addressing food safety.Trends Food Sci Technol. 2024 Nov;153:104725. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2024.104725. Epub 2024 Sep 21. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39665028 Free PMC article.
-
Sound waves alter the viability of tobacco cells via changes in cytosolic calcium, membrane integrity, and cell wall composition.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 11;19(3):e0299055. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299055. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38466667 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study revealed significant SNPs for anthracnose resistance, seed alkaloids and protein content in white lupin.Theor Appl Genet. 2024 Jun 10;137(7):155. doi: 10.1007/s00122-024-04665-2. Theor Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 38858311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed I. M., Nadira U. A., Qiu C. W., Cao F. B., Zhang G. P., Holford P., et al. (2018). Tolerance to drought, low pH and Al combined stress in Tibetan wild barley is associated with improvement of ATPase and modulation of antioxidant defense system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19: 3553. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113553 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

