Lentiviral vector transduction provides nonspecific immunogenicity for syngeneic tumor models
- PMID: 36161729
- PMCID: PMC9643670
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.23467
Lentiviral vector transduction provides nonspecific immunogenicity for syngeneic tumor models
Abstract
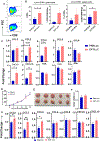
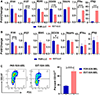
Lentivirus-based transduction systems are widely used in biological science and cancer biology, including cancer immunotherapy. However, in in vivo transplanted tumor model, the immunogenicity of these transduced cells was not appropriately addressed. Here, we used empty vector-transduced mouse melanoma (B16) and carcinoma (lewis lung carcinoma) cells transplanted tumor model to study the immune response due to the transduction processes. We showed that the overall in vivo tumor growth rate gets reduced in transduced cells only in immune-competent mice but not in nude mice. This data indicate the involvement of the immune system in the in vivo tumor growth restriction in the transduced group. Further studies showed that specific activation of CD8+ T cells might be responsible for restricted tumor growth. Mechanistically, transduced tumor cells show the higher activity of type I interferon, which might play an essential role in this activation. Overall, our data indicate the modulation of the immune system by lentiviral vector transduced tumor cells, which required further studies to explore the mechanisms and better understand the biological significance. Our data also indicate the importance of considering the immunogenicity of transduced cells when analyzing in vivo results, especially in studies related to immunotherapy.
Keywords: CD8+ T cells; lentivirus; type I interferon.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interested:
None
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lentivirally transduced dendritic cells as a tool for cancer immunotherapy.J Gene Med. 2003 Aug;5(8):654-67. doi: 10.1002/jgm.400. J Gene Med. 2003. PMID: 12898635
-
Induction of effective therapeutic antitumor immunity by direct in vivo administration of lentiviral vectors.Gene Ther. 2006 Apr;13(7):630-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302697. Gene Ther. 2006. PMID: 16355115
-
Lentivirus-mediated gene transfer and expression in established human tumor antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells and primary unstimulated T cells.Hum Gene Ther. 2003 Jul 20;14(11):1089-105. doi: 10.1089/104303403322124800. Hum Gene Ther. 2003. PMID: 12885348
-
From pathogen to medicine: HIV-1-derived lentiviral vectors as vehicles for dendritic cell based cancer immunotherapy.J Gene Med. 2006 Jan;8(1):3-17. doi: 10.1002/jgm.846. J Gene Med. 2006. PMID: 16288497 Review.
-
Lentiviral vectors for anti-tumor immunotherapy.Curr Gene Ther. 2008 Dec;8(6):438-48. doi: 10.2174/156652308786848058. Curr Gene Ther. 2008. PMID: 19075627 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of iRhom1 by CD44-targeting nanocarrier for improved cancer immunochemotherapy.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 4;15(1):255. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44572-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38177179 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

