Improving Vibrational Spectroscopy Prospects in Frontline Clinical Diagnosis: Fourier Transform Infrared on Buccal Mucosa Cancer
- PMID: 36161799
- PMCID: PMC9558084
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c02496
Improving Vibrational Spectroscopy Prospects in Frontline Clinical Diagnosis: Fourier Transform Infrared on Buccal Mucosa Cancer
Abstract
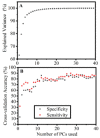
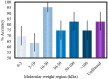
We report a novel method with higher than 90% accuracy in diagnosing buccal mucosa cancer. We use Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of human serum by suppressing confounding high molecular weight signals, thus relatively enhancing the biomarkers' signals. A narrower range molecular weight window of the serum was also investigated that yielded even higher accuracy on diagnosis. The most accurate results were produced in the serum's 10-30 kDa molecular weight region to distinguish between the two hardest to discern classes, i.e., premalignant and cancer patients. This work promises an avenue for earlier diagnosis with high accuracy as well as greater insight into the molecular origins of these signals by identifying a key molecular weight region to focus on.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy in Oral Cancer Diagnosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 26;22(3):1206. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031206. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33530491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential role of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and imaging in cancer diagnosis incorporating complex mathematical methods.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2002 Apr;1(2):95-104. doi: 10.1177/153303460200100201. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2002. PMID: 12622515
-
An empirical evaluation of three vibrational spectroscopic methods for detection of aflatoxins in maize.Food Chem. 2015 Apr 15;173:629-39. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.099. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 25466069
-
Fourier transform infrared for noninvasive optical diagnosis of oral, oropharyngeal, and laryngeal cancer.Transl Res. 2014 Jan;163(1):19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2013.09.006. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Transl Res. 2014. PMID: 24095955
-
Vibrational Biospectroscopy: An Alternative Approach to Endometrial Cancer Diagnosis and Screening.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 27;23(9):4859. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094859. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563249 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Frontline clinical diagnosis-FTIR on pancreatic cancer.Cancer Med. 2023 Aug;12(16):17340-17345. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6346. Epub 2023 Jul 19. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37466344 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of sudden cardiac death from human blood using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and machine learning.Int J Legal Med. 2024 May;138(3):1139-1148. doi: 10.1007/s00414-023-03118-7. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Int J Legal Med. 2024. PMID: 38047927
-
Advancing frontline early pancreatic cancer detection using within-class feature extraction in FTIR spectroscopy.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 22;14(1):28940. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79153-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39578495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NHS . Achieving world-class cancer outcomes: A strategy for England 2015–2020; NHS, 2015.
-
- NHS . Achieving world-class cancer outcomes: A strategy for England 2015–2020; Progress report 2016–17; NHS, 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

