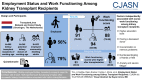
Employment Status and Work Functioning among Kidney Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 36162849
- PMCID: PMC9528259
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05560522
Employment Status and Work Functioning among Kidney Transplant Recipients
Abstract
Background and objectives: To date, employment figures of kidney transplant recipients in Europe are inconsistent. Additionally, little is known about work functioning of employed kidney transplant recipients and work functioning trajectories before and after transplantation.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Data from the ongoing TransplantLines Biobank and Cohort study and from community-dwelling employed adults were used. Health-related work functioning of kidney transplant recipients was assessed with the Work Role Functioning Questionnaire 2.0 and compared with potential kidney donors and community-dwelling employed adults.
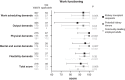
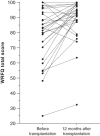
Results: We included 668 kidney transplant recipients of working age (59% men, age 51±11 years) at median 3 (interquartile range, 2-10) years after transplantation, 246 potential kidney donors of working age (43% men, age 53±9 years), and 553 community-dwelling employed adults (70% men, age 45±11 years). The proportion of employed kidney transplant recipients was lower compared with potential kidney donors (56% versus 79%). If employed, the work functioning score of kidney transplant recipients was slightly lower compared with employed potential kidney donors yet higher compared with community-dwelling employed adults (medians 91 [interquartile range, 76-98], 94 [interquartile range, 85-99], and 88 [interquartile range, 79-95], respectively). Backward linear regression analyses revealed that lower educational level, having a kidney from a deceased donor, presence of tingling or numbness of hands or feet, presence of concentration/memory problems, presence of anxiety, and presence of severe fatigue were independently associated with lower work functioning among kidney transplant recipients. Additional subgroup analyses showed that work functioning scores were lower before transplantation than at 12 months after transplantation (83 [interquartile range, 66-93] versus 92 [interquartile range, 88-98], respectively; P=0.002).
Conclusions: Stable employed kidney transplant recipients report to function well at work. In addition, this study shows that self-reported work functioning is higher after successful kidney transplantation compared with before transplantation.
Clinical trial registry name and registration number: TransplantLines Biobank and Cohort study, NCT03272841 PODCAST: This article contains a podcast at https://www.asn-online.org/media/podcast/CJASN/2022_09_26_CJN05560522.mp3.
Keywords: employment status; kidney transplantation; quality of life; side effects of immunosuppressive therapy; work functioning.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Jordakieva G, Grabovac I, Steiner M, Winnicki W, Zitta S, Stefanac S, Brooks M, Sunder-Plaßmann G, Rosenkranz AR, Godnic-Cvar J: Employment status and associations with workability, quality of life and mental health after kidney transplantation in Austria. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17: 1254, 2020 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Modini M, Joyce S, Mykletun A, Christensen H, Bryant RA, Mitchell PB, Harvey SB: The mental health benefits of employment: Results of a systematic meta-review. Australas Psychiatry 24: 331–336, 2016 - PubMed
-
- Waddell G, Burton A: Is work good for your health and well-being? London, The Stationary Office. 2006. Available at: https://cardinal-management.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/Burton-Wadd.... Accessed June 24, 2021
-
- D’Egidio V, Mannocci A, Ciaccio D, Sestili C, Cocchiara RA, Del Cimmuto A, La Torre G: Return to work after kidney transplant: A systematic review. Occup Med (Lond) 69: 412–418, 2019 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

