Persistent Antigen Harbored by Alveolar Macrophages Enhances the Maintenance of Lung-Resident Memory CD8+ T Cells
- PMID: 36162870
- PMCID: PMC9588742
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200082
Persistent Antigen Harbored by Alveolar Macrophages Enhances the Maintenance of Lung-Resident Memory CD8+ T Cells
Abstract
Lung tissue-resident memory T cells are crucial mediators of cellular immunity against respiratory viruses; however, their gradual decline hinders the development of T cell-based vaccines against respiratory pathogens. Recently, studies using adenovirus (Ad)-based vaccine vectors have shown that the number of protective lung-resident CD8+ TRMs can be maintained long term. In this article, we show that immunization of mice with a replication-deficient Ad serotype 5 expressing influenza (A/Puerto Rico/8/34) nucleoprotein (AdNP) generates a long-lived lung TRM pool that is transcriptionally indistinct from those generated during a primary influenza infection. In addition, we demonstrate that CD4+ T cells contribute to the long-term maintenance of AdNP-induced CD8+ TRMs. Using a lineage tracing approach, we identify alveolar macrophages as a cell source of persistent NP Ag after immunization with AdNP. Importantly, depletion of alveolar macrophages after AdNP immunization resulted in significantly reduced numbers of NP-specific CD8+ TRMs in the lungs and airways. Combined, our results provide further insight to the mechanisms governing the enhanced longevity of Ag-specific CD8+ lung TRMs observed after immunization with recombinant Ad.
Copyright © 2022 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures

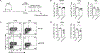
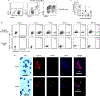


References
-
- Gebhardt T, Wakim LM, Eidsmo L, Reading PC, Heath WR, and Carbone FR. 2009. Memory T cells in nonlymphoid tissue that provide enhanced local immunity during infection with herpes simplex virus. Nat Immunol 10: 524–530. - PubMed
-
- Mackay LK, Wynne-Jones E, Freestone D, Pellicci DG, Mielke LA, Newman DM, Braun A, Masson F, Kallies A, Belz GT, and Carbone FR. 2015. T-box Transcription Factors Combine with the Cytokines TGF-beta and IL-15 to Control Tissue-Resident Memory T Cell Fate. Immunity 43: 1101–1111. - PubMed
-
- Kumar BV, Ma W, Miron M, Granot T, Guyer RS, Carpenter DJ, Senda T, Sun X, Ho SH, Lerner H, Friedman AL, Shen Y, and Farber DL. 2017. Human Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells Are Defined by Core Transcriptional and Functional Signatures in Lymphoid and Mucosal Sites. Cell Rep 20: 2921–2934. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

