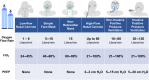
Oxygen as an Essential Medicine
- PMID: 36162911
- PMCID: PMC9417445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccc.2022.06.010
Oxygen as an Essential Medicine
Abstract
Supplemental oxygen is an essential medication in critical care. The optimal oxygen dose delivery system remains unclear, however. The "dose" and "delivery" of oxygen carry significant importance for resource-limited settings, such as low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Regrettably, LMICS often experience significant inequities in oxygen supply and demand, with major impacts on preventable mortality. These inequities have become particularly prominent during the global COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting the need for additional investment and research into the best methods to utilize supplemental oxygen and ensure stable access to medical oxygen.
Keywords: COVID-19; Critical illness; Global health; Oxygen.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Department of Veterans Affairs Tennessee Valley Health Care System Geriatric Research, Education and Clinical Center (GRECC) and VA-MERIT, the National Institutes of Health under awards (R01AG027472, R01AG035117, R01HL111111, R01GM120484, and R01AG058639).
Figures
References
-
- Vincent J.L., Akça S., De Mendonça A., et al. The epidemiology of acute respiratory failure in critically ill patients(∗) Chest. 2002;121(5):1602–1609. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017. The selection and use of essential medicines: report of the WHO Expert Committee, 2017 (including the 20th WHO model list of essential medicines and the 6th WHO Model list of essential medicines for children)
-
- Brugniaux J.V., Coombs G.B., Barak O.F., et al. Highs and lows of hyperoxia: physiological, performance, and clinical aspects. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018;315(1):R1–R27. - PubMed
-
- Davies K.J.A. In: Rice-Evans C., Halliwell B., Lunt G.G., et al., editors. vol. 61. Portland Press; London, United Kingdom: 1995. Oxidative stress: the paradox of aerobic life; pp. 1–31. (Biochemical Society Symposia). - PubMed
-
- Nash G., Blennerhassett J.B., Pontoppidan H. Pulmonary lesions associated with oxygen therapy and artifical ventilation. N Engl J Med. 1967;276(7):368–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical