Radiographic factors associated with inferior alveolar nerve exposure during mandibular third molar surgery and their influence on neurosensory deficit: A prospective study
- PMID: 36164406
- PMCID: PMC9508473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2022.08.025
Radiographic factors associated with inferior alveolar nerve exposure during mandibular third molar surgery and their influence on neurosensory deficit: A prospective study
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding missing declaration of competing interest statements in previously published articles.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2024 Jul-Aug;14(4):351-352. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2024.05.008. Epub 2024 May 22. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2024. PMID: 38826836 Free PMC article.
Abstract
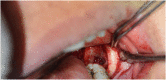
Introduction: The inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) can occasionally be observed in the extraction socket of the mandibular third molar (M3M) intraoperatively. Exposure of inferior alveolar neurovascular bundle during surgery primarily depends upon the absence of bony cortex between the canal and root of impacted third molar or either by existence of a very thin cortical lining between two which gets broken during luxation of tooth. Accurate anatomical relationship of inferior alveolar canal with root apex of impacted (M3M) and the location of canal can be determined by Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Material and methods: Initially 200 patients evaluated by Orthopantomogram (OPG) for anatomical relationship of IAN with impacted (M3M) and various radiographic risk factors for nerve injury. Among these 200, 75 showed the presence of two or more than two risk factors for IAN injury which then were further evaluated by using CBCT for presence or absence of cortex of canal and location of canal on buccal, lingual, inferior, and interradicular position.
Conclusion: Cortex of canal is an important barrier between the root apex and inferior alveolar neurovascular bundle. Interruption of cortex on CBCT, the interradicularly and lingually positioned neurovascular bundle become a strong affirmation for intra operative nerve exposure during (M3M) surgery. Although its exposure is affected by various factors such as bone density, sex and age of patient, surgeon's expertise, operative tissue damage, post operative edema, surgical procedure, but neurosensory deficit do not occur simply after the exposure of neurovascular bundle.
Keywords: Cone beam computed; Cone beam computed tomography, CBCT; Cortex of inferior alveolar canal; Impacted mandibular third molar; Mandibular third molar, M3M; Nerve exposure; Orthopantomography; Orthopantomography, Panoramic radiography, OPG; Paresthesia; Tomography.
© 2022 Craniofacial Research Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Su N., Wijk A.V., Berkhout E., et al. Predictive value of panoramic radiography for injury of inferior alveolar nerve after mandibular third molar surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017 Apr;75(4):663–679. - PubMed
-
- Selvi F., Dodson T.B., Naattestad A., et al. Factors that are associated with injury to inferior alveolar nerve in high risk patients after removal of third molars. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;51:868. - PubMed
-
- Baqain Z.H., AlHadidi A. Cone beam computed tomography: rejuvenating dentistry. Fla Dent J. 2016;7:74.
-
- Ghaeminia H., Meijer G.J., Soehardi A., et al. The use of cone beam CT for the removal of wisdom teeth changes the surgical approach compared with panoramic radiography: a pilot study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;40:834. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

