Diagnostic Performance of Transient Elastography Versus Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography for Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Viral Hepatitis: Direct Comparison and a Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36164448
- PMCID: PMC9509223
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1960244
Diagnostic Performance of Transient Elastography Versus Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography for Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Viral Hepatitis: Direct Comparison and a Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to compare the diagnostic performance of transient elastography (TE) and two-dimensional shear wave elastography (2D-SWE) for staging liver fibrosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis (CVH).
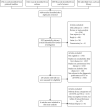
Methods: Pubmed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library were searched (-01/08/2021) for studies comparing TE with 2D-SWE in patients with CVH. Other etiologies of chronic liver disease (CLD) and articles not published in SCI journals were excluded. The bivariate random-effects model was used to pool the performance of the TE and 2D-SWE.
Results: Eight articles with a total of 1301 CVH patients were included. The prevalence of significant fibrosis (fibrosis stage ≥ 2), advanced fibrosis (fibrosis stage ≥ 3), and cirrhosis was 50.8%, 44.8%, and 34.7%, respectively. 2D-SWE expressed higher overall accuracy than TE in detecting significant fibrosis (0.93 vs. 0.85, P = 0.04). No significant difference among the overall diagnostic accuracy of TE and 2D-SWE in staging advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis was found.
Conclusion: TE and 2D-SWE express good to excellent diagnostic accuracies to stage fibrosis in CVH patients. 2D-SWE compares favorably with TE especially for predicting significant fibrosis.
Copyright © 2022 Qing-Tian Luo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

