Efficacy and Tolerability of Hybrid Complexes of High- and Low-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronan Intradermal Injections for the Treatment of Skin Roughness and Laxity of the Neck
- PMID: 36164489
- PMCID: PMC9509274
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4497176
Efficacy and Tolerability of Hybrid Complexes of High- and Low-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronan Intradermal Injections for the Treatment of Skin Roughness and Laxity of the Neck
Abstract
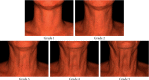
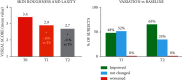
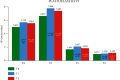
This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of a well-characterized formulation of hyaluronic acid (HA), Profhilo®, in the treatment of roughness and laxity of the neck skin. The study was performed on 25 subjects ranging in age from 40 to 65 years. Two injections of the studied product at 30-day intervals were performed, with evaluations conducted 1 and 4 months after the first injection. The efficacy was determined by clinical and multilevel instrumental evaluations. In addition, at the end of the study, the subjects completed a questionnaire related to the efficacy and tolerability of the product. The studied product was shown to induce a clear and statistically significant improvement in the skin of the neck in all the subjects, with concordant results between the clinical, instrumental, and subjects' evaluations. The positive effects, present after the first injection, were further increased in the second and last evaluation. Notably, the product was reported to have a very high tolerability by both clinicians and subjects. In conclusion, two injections of the studied product safely induced skin amelioration in subjects with mild to moderate neck skin roughness and laxity.
Copyright © 2022 Adele Sparavigna et al.
Conflict of interest statement
LB, AMG, & GB are employees of IBSA Farmaceutici Italia Srl. AS declares that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Humzah D., Tateo A., Siquier G. Multimodal approach to the aging neck. Prime Journal . 2019;9(1)
-
- Fabi S. G., Burgess C., Carruthers A., et al. Consensus recommendations for combined aesthetic interventions using botulinum toxin, fillers, and microfocused ultrasound in the neck, décolletage, hands, and other areas of the body. Dermatologic Surgery . 2016;42(10):1199–1208. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000000869. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

