The Pharmacological Effects of Silver Nanoparticles Functionalized with Eptifibatide on Platelets and Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 36164554
- PMCID: PMC9507977
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S373691
The Pharmacological Effects of Silver Nanoparticles Functionalized with Eptifibatide on Platelets and Endothelial Cells
Abstract
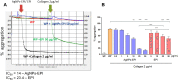
Purpose: In the search for new drug delivery platforms for cardiovascular diseases and coating of medical devices, we synthesized eptifibatide-functionalized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs-EPI) and examined the pharmacological activity of AgNPs-EPI on platelets and endothelial cells in vitro and ex vivo.
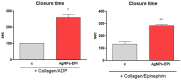
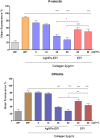
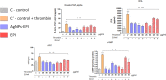
Methods: Spherical AgNPs linked to eptifibatide were synthesized and characterized. Cytotoxicity was measured in microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1), platelets and red blood cells. Platelet mitochondrial respiration was measured using the Oxygraph-2k, a high-resolution modular respirometry system. The effect of AgNPs-EPI on the aggregation of washed platelets was measured by light aggregometry and the ex vivo occlusion time was determined using a reference laboratory method. The surface amount of platelet receptors such as P-selectin and GPIIb/IIIa was measured. The influence of AgNPS-EPI on blood coagulation science was assessed. Finally, the effect of AgNPs-EPI on endothelial cells was measured by the levels of 6-keto-PGF1alpha, tPa, cGMP and vWF.
Results: We describe the synthesis of AgNPs using eptifibatide as the stabilizing ligand. The molecules of this drug are directly bonded to the surface of the nanoparticles. The synthesized AgNPs-EPI did not affect the viability of platelets, endothelial cells and erythrocytes. Preincubation of platelets with AgNPs-EPI protected by mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation capacity. AgNPs-EPI inhibited aggregation-induced P-selectin expression and GPIIb/IIIa conformational changes in platelets. AgNPs-EPI caused prolongation of the occlusion time in the presence of collagen/ADP and collagen/adrenaline. AgNPs-EPI regulated levels of 6-keto-PGF1alpha, tPa, vWf and cGMP produced in thrombin stimulated HMEC-1 cells.
Conclusion: AgNPs-EPI show anti-aggregatory activity at concentrations lower than those required by the free drug acting via regulation of platelet aggregation, blood coagulation, and endothelial cell activity. Our results provide proof-of-principle evidence that AgNPs may be used as an effective delivery platform for antiplatelet drugs.
Keywords: RGD; aggregation; antiplatelet; biocompatibility; coagulation system; drug delivery.
© 2022 Hajtuch et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of functionalized silver nanoparticles on aggregation of human blood platelets.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Sep 11;14:7399-7417. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S213499. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31571858 Free PMC article.
-
Incomplete inhibition of platelet aggregation and glycoprotein IIb-IIIa receptor blockade by abciximab: importance of internal pool of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa receptors.Thromb Haemost. 2000 Jun;83(6):915-22. Thromb Haemost. 2000. PMID: 10896249
-
The in vitro effect of eptifibatide, a glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonist, on various responses of porcine blood platelets.Acta Pol Pharm. 2009 May-Jun;66(3):235-42. Acta Pol Pharm. 2009. PMID: 19645323
-
The role of the platelet in the pathogenesis of atherothrombosis.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2005;5(6):399-408. doi: 10.2165/00129784-200505060-00007. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2005. PMID: 16259528 Review.
-
Platelet aggregation inhibition with glycoprotein IIb--IIIa inhibitors.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2001 Apr;11(2):99-110. doi: 10.1023/a:1011216414539. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2001. PMID: 11406724 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress of nanomaterials in the treatment of thrombus.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 May;14(5):1154-1172. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01478-6. Epub 2023 Nov 25. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38006448 Review.
-
Synthesis, characterization and application of silk sericin-based silver nanocomposites for antibacterial and food coating solutions.RSC Adv. 2024 Oct 21;14(45):33068-33079. doi: 10.1039/d4ra07056a. eCollection 2024 Oct 17. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39435006 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

