In silico prediction of COVID-19 cytokine storm in lung cancer types
- PMID: 36164562
- PMCID: PMC9492516
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101350
In silico prediction of COVID-19 cytokine storm in lung cancer types
Abstract
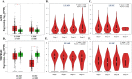
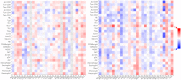
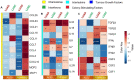
Lung cancer is one of the most frequently diagnosed malignant tumors and the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Mainly, Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which accounts for more than eighty-five percent of all lung cancers, consists of two major subtypes: lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC). Novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) affected millions of people caused by acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2) around the globe. Lung cancer patients and COVID-19 present unique and unfortunate lethal combinations because the lungs are the primary target organ of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clinical studies have demonstrated that an over-activated inflammatory response associated with severe COVID-19 cases is characterized by excessive auto-amplifying cytokine release, which is defined as a "cytokine storm." ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors play an essential role in SARS-CoV-2 infection; therefore, using in silico analysis, we did correlation analysis with immune infiltration markers in LUAD and LUSC patient groups. Our study identified a promising correlation between immune-modulators and receptor proteins (ACE-2 and TMPRSS2), creating a domain that requires further laboratory studies for clinical authentication.
Keywords: ACE-2; COVID-19; Cytokine storm; Immune-modulators; Lung cancer; TMPRSS2.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In silico analysis identifies neuropilin-1 as a potential therapeutic target for SARS-Cov-2 infected lung cancer patients.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jun 24;13(12):15770-15784. doi: 10.18632/aging.203159. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34168096 Free PMC article.
-
Structural variations and expression profiles of the SARS-CoV-2 host invasion genes in lung cancer.J Med Virol. 2020 Nov;92(11):2637-2647. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26107. Epub 2020 Jun 19. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32492203 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of two potential novel SARS-CoV-2 entries, TMPRSS2 and IFITM3, in healthy individuals and cancer patients.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Sep 30;16(15):3028-3036. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.51234. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33061814 Free PMC article.
-
Tocilizumab in SARS-CoV-2 Patients with the Syndrome of Cytokine Storm: A Narrative Review.Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2021;16(2):138-145. doi: 10.2174/1574887115666200917110954. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2021. PMID: 32940187 Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of P2X7 Purinergic Receptor Modulation in the Main Organs Affected by the COVID-19 Cytokine Storm.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(22):1798-1814. doi: 10.2174/1381612828666220713115906. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 35838210 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

