Cost-effectiveness of Ribociclib in HER2- negative breast cancer: A synthesis of current evidence
- PMID: 36164576
- PMCID: PMC9508637
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.06.002
Cost-effectiveness of Ribociclib in HER2- negative breast cancer: A synthesis of current evidence
Abstract
Background: The main aim of this study was to investigate the cost-effectiveness of Ribociclib in the treatment of patients with breast cancer by assessing the published evidence.
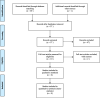
Method: A systematic review of the published literature was conducted to identify the economic evaluations/cost-effectiveness study of Ribociclib. In this study, several databases were inspected, including PubMed, NHS Economic Evaluation, Cochran, and Scopus. Studies were eligible if they assessed the cost-effectiveness of Ribociclib and reported incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER). The study was performed and conducted following the PRISMA reporting guidelines.
Results: Of 70 studies identified, 8 articles meet our inclusion criteria. The cost-effectiveness threshold varied from $24,144.18 in Spain to $198,000/QALY in the USA. Moreover, the result demonstrated that the mean ICER varied across different countries $1,863.47/QALY in Spain and $813,132/QALY in the USA.
Conclusion: Among all CDK4/6 inhibitors medications, current evidence indicated that the use of Ribociclib for HER2- negative breast cancer management was beneficial and considered to be cost-effective. Future research is needed to investigate the role of Ribociclib in long-term treatment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CDK4/6 inhibitors; Cost-effectiveness; Economics evaluation; Ribociclib; Systematic review.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Barbieri M., Drummond M., Rutten F., Cook J., Glick H.A., Lis J., Reed S.D., Sculpher M., Severens J.L. What do international pharmacoeconomic guidelines say about economic data transferability? Value in Health. 2010;13(8):1028–1037. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Dikshit R., Eser S., Mathers C., Rebelo M., Parkin D.M., Forman D., Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359–E386. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira, L., Ferreira, P., 2014. Health state values and country-specific value sets. Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer, pp. 2744–2749.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous